Cannabis farmers have been debating which cannabis plant is better for growing – autoflower plants or photoperiods – since the dawn of modern commercial production. Although that debate has heated up more recently with technological advances, both types of plants can produce great harvests if handled properly.
In this blog post, let’s take a look at the differences between autoflowers and photoperiods so we can answer the question: Which type of weed plant should you grow?
Contents
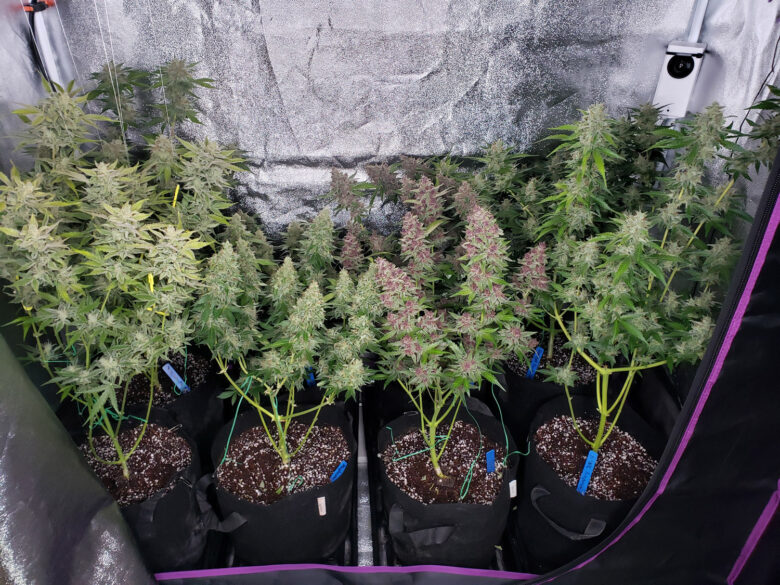
What is an Autoflower Cannabis Plant?

Source: growweedeasy.com
Autoflower plants are special cannabis plants because they don’t require a change in the light cycle to flower. They will automatically switch from growing vegetative buds to flowering buds under any light schedule, regardless of the number of hours of dark and light.
The autoflower plants are achieved by crossing Cannabis Ruderalis (a wild cannabis species) with other marijuana strains, most commonly Indica or Sativa types. Cannabis Ruderalis, also known as Rudy, originates from the colder climates of Central and Eastern Europe. When the crossing is completed, the new plant will flower based on age and not on a light cycle.
This cannabis plant adopts the Ruderalis trait of self-flowering and is capable of producing buds regardless of the hours it gets in complete darkness.
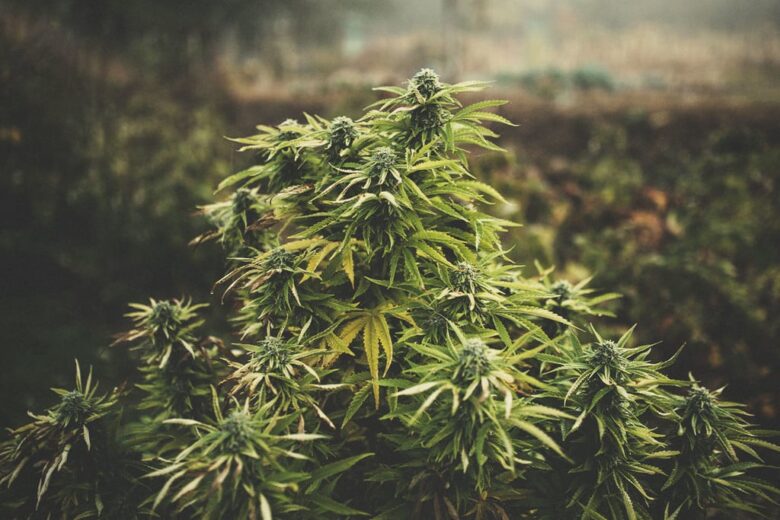
What is a Photoperiodic Cannabis Plant?

Source: royalqueenseeds.com
Photoperiods are the traditional cannabis varieties. They’ve been around since before autoflowers and have been perfected over decades of selective breeding. As the name suggests, these plants require a specific photoperiod, or amount of light and darkness, to determine when they flower.
Typically, photoperiodic cannabis plants require 18 hours of light in the vegetative stage and 12 hours of darkness to flower. This photoperiod must be strictly followed, or else you risk delays in flowering and lower yields.
Due to their strict nature, photoperiods are usually grown outdoors in summer. This ensures the plants get enough light to flower and won’t be killed by the cold winter weather.
So which is better? Autoflower vs Photoperiod Cannabis?
To answer this question, we will explore the differences between these two types of cannabis plants. Based on the differences, you can decide which type of plant is better for you.
Autoflower vs Photoperiod Cannabis: Main Differences
For a cannabis plant to move from the vegetative stage to the flowering stage, numerous factors come into play. We will categorize the main differences between autoflower and photoperiod plants by these factors: flowering time, yield, plant size, potency, cloning, cost of cultivation, and maintenance.
Flowering Time
Source: vivosun.com
Autoflowers tend to flower faster than photoperiods since they do not rely on light cycles. Normally, they reach the flowering stage 4-5 weeks after seed germination. Photoperiods, on the other hand, take about 8-9 weeks to reach the flowering stage. This is what makes autoflowers move from seed to harvest much faster.
Although environmental factors can delay flowering, plant genetics greatly influence flowering time. Plant genetics will determine how long the plant takes to flower regardless of whether it is an autoflower or a photoperiod.
Yield
When investing in cannabis cultivation, you are likely to be concerned about the yield. Autoflowers produce lower yields than photoperiods, with an average yield of around 10-50 grams per plant. This is mainly attributed to the shorter vegetative and flowering periods.
Photoperiods are known to produce higher yields. A photoperiod can produce one gram of yield for every watt of light. This means that if you allow your photoperiod cannabis plant 600 watts of light, it can produce up to 600 grams of yield per plant. Ensuring the photoperiods have at least 18 hours of light daily will help maximize yields.
However, when factoring in the yield of both types of plants, it is important to consider the number of harvests per year. Autoflowers, with their faster flowering time and lower yields, can be harvested up to 4 times a year. With their longer flowering time and higher yields, photoperiods can only be harvested about once or twice a year.
So, depending on your needs, either one could be the winner regarding yield.
Plant Size

Source: i49.net
Autoflowers usually stay shorter and bushier than photoperiods. When grown indoors, autoflower plants can reach a height of around 2-3 feet. In outdoor environments, they can reach a height of up to 5 feet. This means that autoflowers are more suitable for growing in limited spaces.
Photoperiods are known for their ability to grow tall and lanky. Photoperiods can reach heights of 5-6 feet when grown indoors, while outdoor plants can reach 9-10 feet. If you have enough space to accommodate the height of photoperiods, you can maximize yields.
Potency
The main aim of cannabis cultivation is to produce strong and potent yields. Autoflowers tend to have lower THC levels than photoperiods. Most autoflowers will have up to 15-20 per cent THC. On the other hand, photoperiods can have THC levels of over 30 per cent when grown properly. This makes photoperiods stronger than their autoflower counterparts.
Autoflowers have lower THC since Cannabis Ruderalis, which is used to produce autoflowers, has lower THC levels than Indica and Sativa. Therefore, if your aim is to produce a less potent but faster-growing plant, an autoflower would be the best choice.
Cloning

Source: organitek.com
Cloning cannabis plants involves taking a cut from the mother plant and growing it. Making cannabis clones is an alternative method for producing new plants. Photoperiods are easier to clone than autoflowers. Autoflowers do not respond well to cloning due to their short flowering time and smaller size.
You can duplicate photoperiods because they can be kept in the vegetative stage for long periods. Autoflowers do not stay in the vegetative state for as long, so cloning them is difficult.
Cost of Cultivation
The cost of cultivating cannabis plants depends on the setup you choose. Autoflowers are usually cheaper than photoperiods since they require fewer resources and take up less space. Photoperiods require higher amounts of light and space, making them more expensive to cultivate.
Moreover, autoflowers can thrive easily in less nutrient-rich soil. Photoperiods require nutrient-dense soil and higher levels of nutrients to maximize yields.
Maintenance

Source: cropkingseeds.com
While maximizing yields, you do not want to forget about maintenance. Autoflowers are easier to maintain than photoperiods since they have shorter flowering times and smaller sizes. Photoperiods require more attention to maximize their yields, so they must be monitored more frequently.
You must ensure the photoperiods receive at least 18 hours of light daily. Additionally, you must also ensure that there are no light leaks to prevent disruptions in the light cycles. This makes photoperiods a bit harder to maintain.
Conclusion
Now that you know the main differences between autoflower vs photoperiod cannabis, it is up to you to decide which type of plant is better for you. Autoflowers are faster to grow and require less maintenance but have lower yields and potency. Photoperiods are harder to maintain, but they produce higher yields and potency. Consider your needs carefully before making a decision.
Good luck!
