If you’ve been feeling the pinch in your wallet every time you go to the store even for the most basic necessities, you’re not imagining it. And if you really feel the pinch when you pay your insurance premiums, rest assured, you’re not alone. The year 2024 has seen a significant uptick in insurance costs across several sectors, far outpacing the usual inflation-related increases in prices of day to day goods. But why is this happening? Let’s delve into the reasons behind this surge and try to make sense of it all.

Source: insurance.ohio.gov
Contents
Car Insurance: A Bumpy Ride
The costs of insuring your car have been on a steep uphill trajectory throughout 2024, with rates of various coverage options expected to increase as much as 8.4% nationwide. This is the steepest percentage increase in over six years, signaling a distressing trend for car owners across the country.
A multitude of factors are driving this increase. Because of climate change, weather-related events, such as floods, wildfires, and tornadoes, have once again been on the rise, leading to increased damage to vehicles. At the same time, after years spent at home during the pandemic, many employees are finally returning to workplaces, resulting in increased road usage and, consequently, higher accident rates.
Furthermore, the overall costs associated with cars have seen a sharp increase, in general, over the past few years. With inflation hitting hard across all sectors, new car costs have been driven up by 8-9%, and items like tires have seen a surge in prices by over 10%. Additionally, the costs to repair vehicles have skyrocketed due to inflation, staff shortages, and supply chain issues that are affecting many areas of the country, so this too has a knock on effect on motoring insurance.

Source: canva.com
Home Insurance: The Price of Safety
It’s not just motoring insurance, though. Home insurance has also been hit hard in 2024. Homeowners are seeing an average increase of as much as 12.1% in their insurance premiums, which is obviously a significant uptick compared to most years where changes are minor or even nonexistent. So why so huge an increase, even considering inflation?
The reasons for this surge are diverse. One major driver is the inflationary pressure that’s impacting commodity pricing for materials like steel, lumber, and copper, essential for home construction and repair. So, with inflation badly affecting each component of which houses are made, it’s no surprise that the overall effect is pretty tremendous. Furthermore, to add to the increase in price in raw materials, there’s been a severe shortage of skilled labor in the construction field, primarily due to an increase in home renovations as people choose to improve their current home rather than venture into the exorbitant housing market.
Another factor is the rising cost of both new and pre-owned houses, which jumped over 11% in 2022 in many parts of the country, which is a significant increase after the past few years saw the real estate market in a state of depression. This price increase in the houses themselves obviously directly impacts the costs of home insurance since more valuable homes generally cost more to insure, by definition.
Between all these different factors, unfortunately, there was just no way that home insurance premiums weren’t going to get a lot worse, very quickly.

Source: canva.com
Health Insurance: An Unhealthy Trend
Health insurance premiums have also risen in 2024, with increases recorded in 36 states. This is no doubt an especially large surprise to most people as they might think that being past the pandemic should mean greatly reduced rates. Sadly, that is certainly not the case. In fact, it’s quite the opposite.
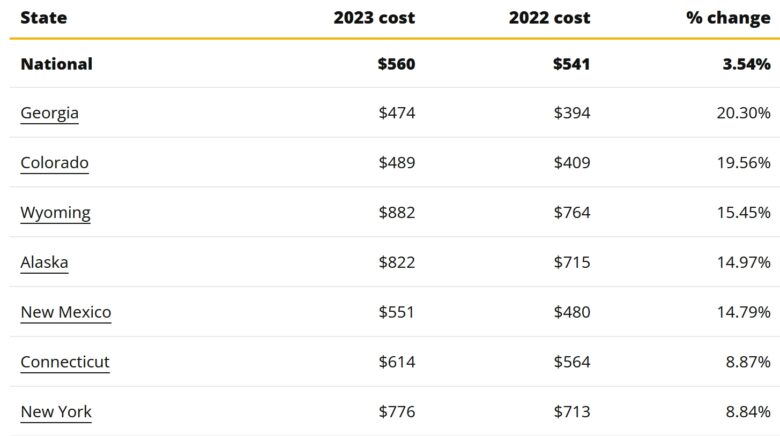
For a 40-year-old, say, on a silver plan—considered the most common tier—purchased through the Healthcare Marketplace, the average premium will be $560 per month. This represents a 4% increase over the previous year and only makes what is an already prohibitively high price for health insurance only that much more difficult for the working class to afford.
Certain states, though, are bearing the brunt of these increases more than others. The five states that are hardest hit, Georgia, Colorado, Wyoming, Alaska, and New Mexico, are expected to see steep increases in their average monthly premiums. In Georgia, for instance, the average premium is projected to rise by a staggering 20.30% from the previous year, which may well cause a great many people to give up their health insurance completely, which can be devastating on so many levels.
It’s important to note that premiums are set based on insurers’ expectations of who will enroll. A younger, healthier population is cheaper to insure than an older one with chronic health conditions. Additionally, insurance companies factor in the rates they’ve been able to negotiate with healthcare providers. Fewer hospitals in a state can mean less competition for favorable rates, thereby leading to higher premiums.
Source: valuepenguin.com
Life Insurance: Living Costs
Lastly, life insurance is also experiencing an uptick in costs. The average annual premium for a 30-year term life insurance policy for a healthy 30-year-old is set to increase by an average of 8% in 2024. This means that the average annual premium will be around $1,080, compared to $1,000 in 2022.
The reasons behind this increase are diverse, but a major factor is the long-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. This global health crisis has led to increased mortality rates, leading insurance companies to reassess their risk models. This reassessment often results in higher premiums for policyholders.

Source: canva.com
Conclusion
In conclusion, 2024 has been a challenging year for insurance policyholders. From cars to homes, health, and life, insurance costs have risen across the board. While this trend is indeed concerning, understanding the factors behind these increases can help us navigate this landscape more effectively. We can only hope that the market conditions improve in the coming years, bringing relief to policyholders around the country. But until then, being knowledgeable about the dynamics at play will allow us to make informed decisions about our insurance needs.
