The aging process is a natural part of life, but the effects of age-related health issues can be significantly reduced with the help of nutrition and supplements. Vitamin D is an essential nutrient for optimal health throughout life, but many adults over 65 have an elevated risk for deficiency due to decreased sun exposure, diminished dietary sources, and reduced absorption ability. Scientific research has revealed an array of ways vitamin D can positively influence physical and mental well-being as we get older. By understanding the role of vitamin D in aging, you may be able to reduce your risk for age-related diseases and better manage existing symptoms.
Source: squarespace.com
Contents
Overview of Age-Related Health Issues
As people age, their bodies are more susceptible to a number of age-related health issues. These issues can range from an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and cancer to developing Type 2 diabetes and osteoporosis. Other common age-related health conditions include Alzheimer’s disease, cataracts, macular degeneration, hearing loss, arthritis, and COPD.
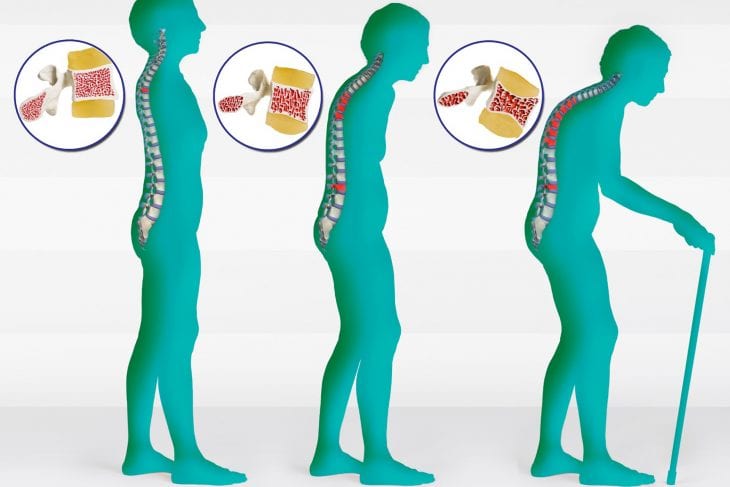
CVD is the leading cause of death in the developed world, accounting for over 80% of all deaths in the United States. Type 2 diabetes is also on the rise among seniors due to a combination of poor diet choices and a lack of physical activity in later life. Osteoporosis is also becoming increasingly common as people age due to calcium deficiency as well as limited exposure to sunlight which can affect bone density.
It is important to remain proactive in preventing these diseases by following a healthy lifestyle including regular exercise, eating nutritious foods that are low in saturated fat and added sugar, avoiding smoking, and engaging in social activities on a regular basis.
Source: medium.com
Vitamin D Deficiency and Aging
Vitamin D plays a critical role in aging and disease prevention, as it is known to help regulate calcium metabolism, support strong bones, and protect against conditions such as osteoporosis, cognitive decline, and certain cancers. Unfortunately, it is estimated that at least 1 billion people globally are deficient in vitamin D, making supplementation increasingly popular for boosting health in later life.
Aging has been associated with an increased risk of low serum vitamin D levels due to a number of reasons including decreased levels of exposure to sunlight, impaired absorption from decreased intestinal absorption capacity, or due to chronic health conditions that can interfere with the body’s capacity to absorb or use available vitamin D25. This deficiency should be considered among the many factors driving age-related diseases such as sarcopenia (loss of muscle mass), osteoporosis (weakening of bones), and frailty. To learn more about this, visit https://centertrt.org/blog/whats-the-difference-between-vitamin-d-and-vitamin-d3.html

Source: canva.com
Why is it beneficial for Age-Related Health Issues?
Vitamin D helps regulate bodily functions and can have a positive impact on healthy aging. It may help reduce the risk of developing age-related diseases, like osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease, as well as mental illness and depression. It also helps promote basic metabolic functions in the body, such as calcium absorption, support for strong bones, energy metabolism, regulation of immunity, and cardiovascular health.
Adequate amounts of vitamin D can also help maintain muscle strength and reduce inflammation associated with aging. Studies have found that higher levels of vitamin D correspond with a reduced risk of age-related diseases and frailty due to better-functioning muscles. In addition, vitamin D supplementation has been studied extensively for its ability to improve bone health in older adults at risk for frailty from osteoporosis or other bone loss disorders.
Other potential benefits include improved cognitive abilities (particularly amongst older adults) as well as stronger physical endurance needed for daily routines like shopping or engaging in leisure activities outside the home such as walking or gardening. It’s important to note that additional clinical studies are needed before any claims can be made about how much benefit supplementing with Vitamin D actually provides regarding the prevention or treatment of age-related illnesses or conditions.

Source: respectfood.com
Intake Recommendations
The National Institutes of Health recommends that adults 50 and older consume 400-800 international units (IU) of vitamin D per day. However, people who are housebound or get very little sun exposure may need as much as 1,000 IU per day to maintain normal blood levels of vitamin D.
It’s best to include nutrient-rich foods in the diet such as salmon and sardines, which are packed with the vitamins D3 and D2, respectively. High-fat dairy products such as milk and yogurt also serve as good sources of vitamin D, as well as some fortified breakfast cereals.
Additionally, Supplemental forms of vitamin D are also recommended for adults more than 50 years old who cannot meet their dietary needs for this essential nutrient. There are two forms available over the counter – cholecalciferol (D3) and ergocalciferol (D2). Research shows both can be safely used to increase and maintain adequate levels of this important nutrient in aging bodies; however, cholecalciferol may provide other health benefits besides just maintaining healthy bones like reducing inflammation and helping with cognitive improvement while ergocalciferol may not offer all these benefits.
Additionally, when choosing a supplement it is important to remember that a multivitamin usually contains 400 IUs of both Vitamins A and E which together can increase the risk for certain illnesses if both vitamins are taken at too high a dose; therefore it is important to keep supplementation doses low when coupled with these vitamins.

Source: e7sby9sd2m5.exactdn.com
Conclusion
In conclusion, research is suggesting that vitamin D has a positive role to play in aiding with age-related health issues. As more studies are conducted, the link between Vitamin D and improvement in overall aging will become clearer. It is clear, however, that supplementing a healthy diet with adequate vitamin D levels can improve physical and mental health in people of all ages.
The most critical aspect of maintaining adequate vitamin D levels is through food sources including fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified milk, and cereal products, and exposure to sunlight. Vitamin D supplements are also available but should be taken under the supervision of a healthcare professional. If you feel your diet or sun exposure is not meeting your vitamin D needs, increasing your intake may benefit you in the long term.
