Molecular therapeutics deal with the various ideas and methods of drug discoveries that are mainly target-specific drugs or induced drugs. Therefore, to make target-specific drugs, the use of research liquids is mandatory in the fields of molecular therapeutics.
The properly conditioned research liquids are quintessential for therapeutic methods and are quite challenging. Hence, to buy research liquids, from the proper source is necessary for the foundations.
This article will discuss the therapeutic applications of research liquids and the various consistencies in which it is available.
Contents
Solvents

Source: wiki.anton-paar.com
Research liquids are used as solvents for dissolving various drugs to administer either intravenously or orally. Sometimes, they are used to dissolve various reactants, drugs, and certain impurities during any kind of purification or manufacturing process. The widely used research liquids that are used as solvents are ethanol and methanol to dissolve any drugs or other solutes during the synthesis process.
Water is also used with research liquids to dissolve drugs to make them infusible or injectable.
Proper solvent selection is critical in drug formulation to ensure stability, enable administration through desired routes, and optimize bioavailability. Research liquids used as solvents must also have acceptable toxicity profiles for the intended use. Following dissolution, techniques like spray drying or lyophilization may be applied to remove the liquid component and transform solutions into powders suitable for encapsulation or tableting.
Molecular Carriers
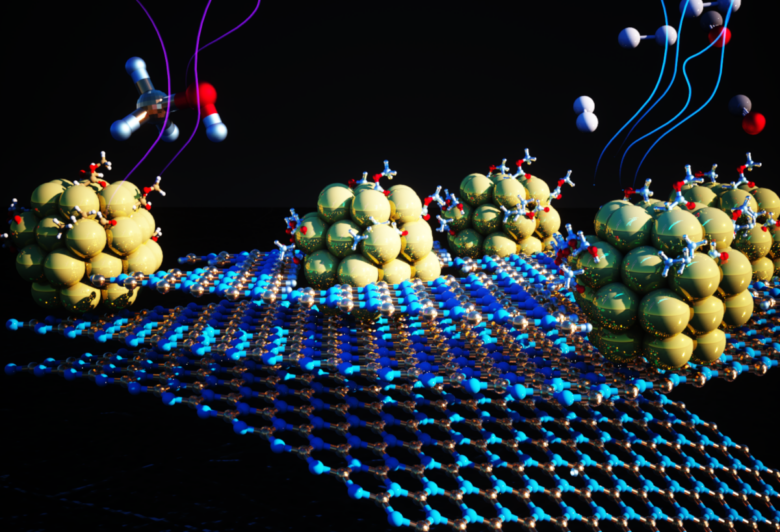
Source: newscenter.lbl.gov
The research liquids are sometimes used as molecular carriers to deliver certain therapeutic molecules to specific targets. Research liquids protect the drugs from any kind of enzymatic degradations or lytic activities by encapsulating them. Liquids also facilitate the transportation through various organelles without any hindrances.
A prominent example of molecular carriers is liposomes that are synthesized from research liquids. These are small molecular vesicles that encapsulate the delivered drug to the specific target.
Other carrier systems like micelles, dendrimers, nanoemulsions, and hydrogels depend on specialty research liquids tailored to the drug and delivery goals. These provide key advantages of improving solubility, bioavailability, and controlled release.
Nanoparticles
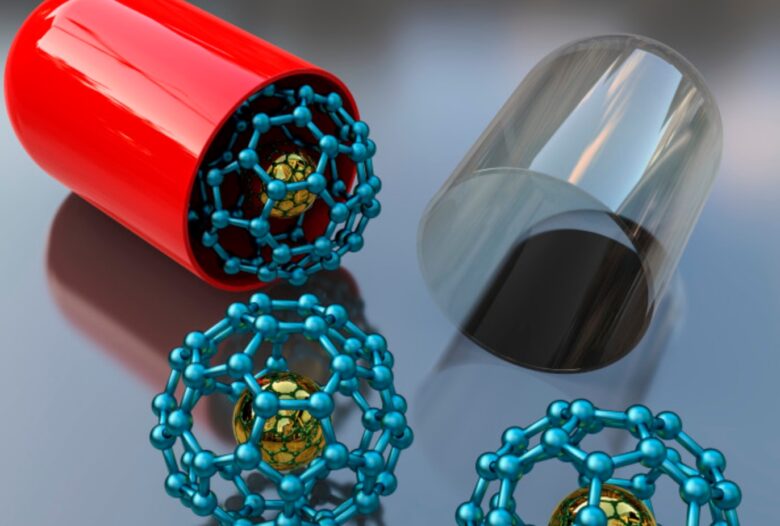
Source: imperial.ac.uk
Nanoparticles are potential drug carriers that are synthesized by using research liquids like polymers, lipids, and certain metals. They can be used easily for various target-specific drug delivery with minimum effect on the other healthy cells. These are currently under investigation to understand their mechanism of action. But it can be efficiently used as a potential drug carrier in the near future.
Nanoparticles have size ranges from 1 to 100 nanometers, which allows them to circulate through blood vessels and accumulate in certain tissues such as tumors. Their small size also results in a high surface area to volume ratio, allowing more drug to be loaded per nanoparticle. Additionally, nanoparticles can be designed to respond to certain stimuli at target sites, causing them to release their drug payloads.
Reaction Media
Source: indianactsi.org
Research liquids can be used as a reaction media for various synthetic and analytical processes in molecular therapeutics. These provide suitable conditions for the microorganisms or mammalian cells to grow with proper micronutrients. Sometimes, they provide conditions for chemical reactions in various purification processes like synthetic or enzymatic reactions.
These can be both organic solvents or aqueous solvents on the basis of the required reaction process. Research liquids in the form of reaction media is predominant in almost every lab as it is the key foundation to conduct a proper experiment. The media generally reduces the reaction time of the various processes and induces the reaction rate of the processes for a better yield of the by-products.
High-Throughput Screening

Source: worldpharmatoday.com
High-throughput screening relies on specially optimized research liquids to test thousands of drug candidates in biological assays. Screening buffers maintain physiological pH to preserve protein targets and cell cultures during rapid compound screening. DMSO ensures solubility while minimizing interference in detection methods like fluorescence. Plate coatings also influence liquid behavior in wells during robotic liquid handling.
In hang drop vapor diffusion for X-ray crystallography, research liquids create a closed system to concentrate proteins into ordered crystals revealing 3D structural insights gently. HTS research liquids enable phenotypic screens to discover new targets and structure-based drug design approaches.
Biologics Formulation

Source: biopharminternational.com
The advent of modern biotechnology has expanded therapeutic options beyond small molecules to encompass complex macromolecules like peptides, proteins, antibodies, nucleic acids, and cellular therapies. However, these biologics impart unique sensitivities and challenges for drug development.
Fortunately, tailored research liquids facilitate these large and delicate molecules’ stabilization, delivery, and testing. Amino acids, carbohydrates, and specialized buffers maintain folding and conformation. Surfactants and viscosity modulators improve solubility and allow controlled release. Growth factors, hormones, antioxidants, and carriers safely convey cells or genes to therapeutic sites of action.
Clinical Trials

Source: recipes.heart.org
Before a drug reaches patients, it must undergo strict clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Each phase depends critically on research liquids enabling administration, blinding, placebos, and consistency across multiple generated lots.
Phase I trials establish pharmacokinetics, dosing, and adverse events in healthy volunteers through research liquids tailored to the molecule’s properties. Subsequent Phase II and Phase III studies recruit real-world patients, using larger batches of research liquids for randomization and blinding to eliminate bias when assessing therapeutic outcomes.
Throughout development, research liquids ensure chemical stability, purity, and potency up to regulatory approval and product launch. Even after marketing, they facilitate continuous manufacturing improvements over a therapy’s lifetime.
Final Remarks
The research liquids play a critical role in molecular diagnostics or molecular therapeutics. These are quite essential for the purification, synthesis, and formulation of various synthetic molecules or drugs. That can be used for efficient drug deliveries or enzymatic pathogen diagnosis. The applications of research liquids span the entire range of the pharmaceutical pipeline.
The innovative ways of liquid formulations are under investigation and are ongoing research topics, which will lead to highly efficient drug delivery and improved therapeutic safety and measures.
