The rapid prototyping industry is undergoing a lot of fundamental and revolutionary changes. One of these changes is the emergence of low volume manufacturers. Product developers are gradually moving away from mass production and towards low volume manufacturing. If you want to know more, please visit the website.
Thanks to the availability of advanced computer software and 3D printing, manufacturers are able to produce customized orders in faster time than ever before, and companies can get their products to the market in weeks rather than months. To be able to keep up with demand, many production lines have turned to the strategies.
Low volume manufacturing is usually used to refer to when a production line produces from as little as 50 to as much as 100,000 pieces. Low volume production acts as a bridge between one-off prototyping and full volume production. A low-volume manufacturer offers a production line which mass produces quality parts in a small volume.
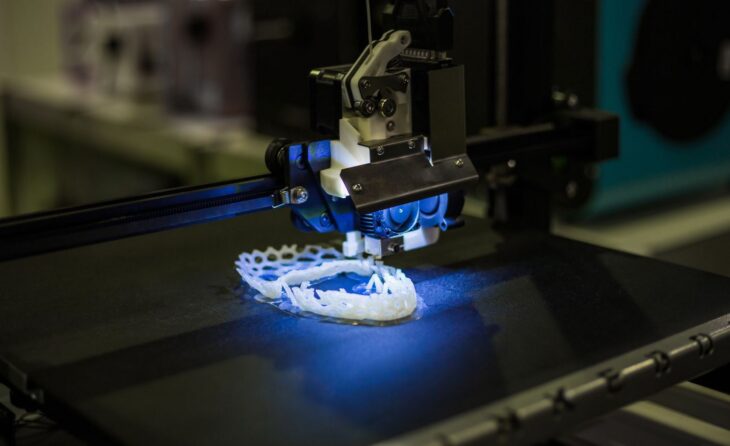

Source: SEA-LECT Plastics
Contents
Why is Low Volume Manufacturing Becoming More Popular?
It not only allows companies to invest less time and money into tooling and materials, but also provides the end products to faster access to consumers. Small volume production helps companies move their product faster from concept to completion.
Other advantages from small batch manufacturing include shorter product life cycles and rapid response to CNC machining. It also shortens overall production lead times and this also allows for time and energy to be saved in product development.
Benefits of Low Volume Manufacturing
Although it sounds counter-intuitive, producing less can actually benefit the company. Here are some reasons why;
Design Flexibility
Complex computer softwares are able to create prototypes very quickly before the company makes an actual prototype. After the prototype is made, a small amount of the pieces are made and sent down the production line for inspection.
During the inspection, if any changes need to be made, the production run is stopped and they are made. With the help of 3D printing customized orders and changes in design can be made and viewed in real-time. This process enables the low volume manufacturer not to have a warehouse full of unusable products due to failure in the initial design.
Source: UL Prospector Knowledge Center
Saves Money
It helps companies to save money in a few ways. If a company is to invest in tool steel, a special kind of hardened steel that is needed to make the machines that produce products. It will cost a lot of money to make a large production run.
Once the low volume manufacturer knows they need a smaller number of pieces, machinery can be made out of less durable steel in order to save money. Worn out parts can be replaced as needed. This helps to save money and lower the overhead on the order.
Provides an Option for Bridge Production
If a low-volume manufacturer impresses a customer with the low volume line, steady orders might be made for years to come. It provides a way for the manufacturer to eventually scale up to full-scale production and also eliminates the use of special machines. When a customer is impressed with the low volume production, it could easily turn into high volume production and more revenue for the low volume manufacturer.
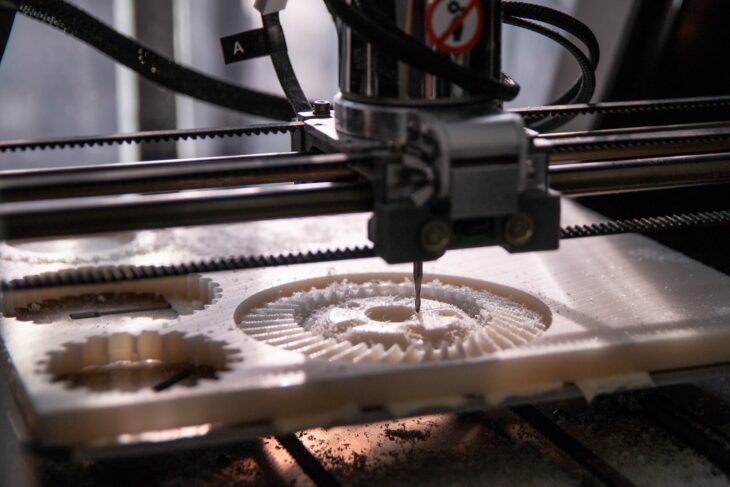

Source: medium
Surpassing the Competition
Using low volume manufacturing, the time to market pieces is reduced and therefore gives the company a competitive edge. Getting their products on shelves faster allows companies to also make money on short-term trends or fads.
Low volume manufacturing also reduces risk because the initial investment is also low. As technology grows and becomes more adaptable to market trends, more profits will be realized from this practice.
Low Volume Manufacturing in the Rapid Prototype Industry
A rapid prototype is a very fast way to verify any aspect and function in the design of a product. They are widely used for business proposals to be shown to potential investors and customers. They can be completed in a matter of days which makes them excellent to be used for any changes.
Low volume manufacturing is a major component of the rapid prototype industry especially in CNC machining as it not only gives a way for a number of prototypes to be made and shown to customers and investors but it is also more cost and labor efficient.
As a member of a production team, engineer, or even an industrial designer, rapid prototyping offers distinct advantages like;
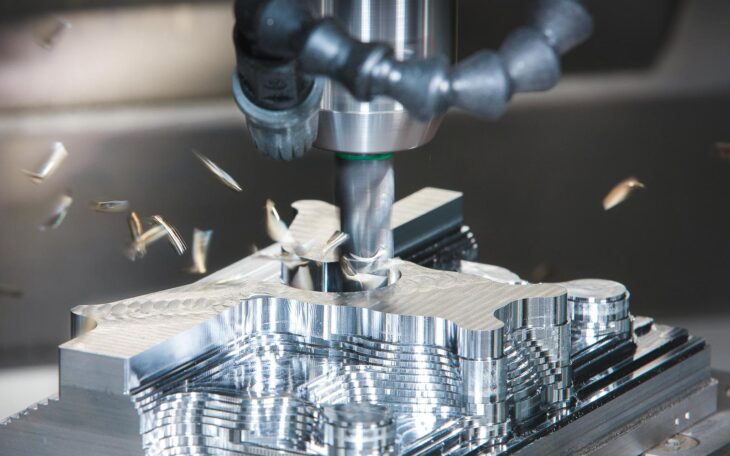

Source: 3dhubs
- Ability to explore concepts in a cost-effective and quick way. This allows you to go far beyond the visualization of the idea, making it very easy to grasp the design of the product in the real world.
- Ability to physically showcase different concepts effectively as a hands-on product to clients.
- Ability to fully test and refine a concept. Using a small series rapid prototype run allows for design flaws that might be costly to be minimized.
- It allows for functional testing and improved evaluation of the product. It ensures that the design is foolproof and optimized.
- It helps to save time and money by removing any need for setup and tooling.
Types of Low Volume Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is also known as 3D printing and can be used to create functional prototypes, plastic models, and use-end production parts. It can be used to create complex geometries, one-off parts, and small batches.
CNC Prototyping
This is ideal for manufacturing high-quality metal or plastic prototype parts. It allows for parts with tighter tolerances and better surface finishings than other prototyping methods.
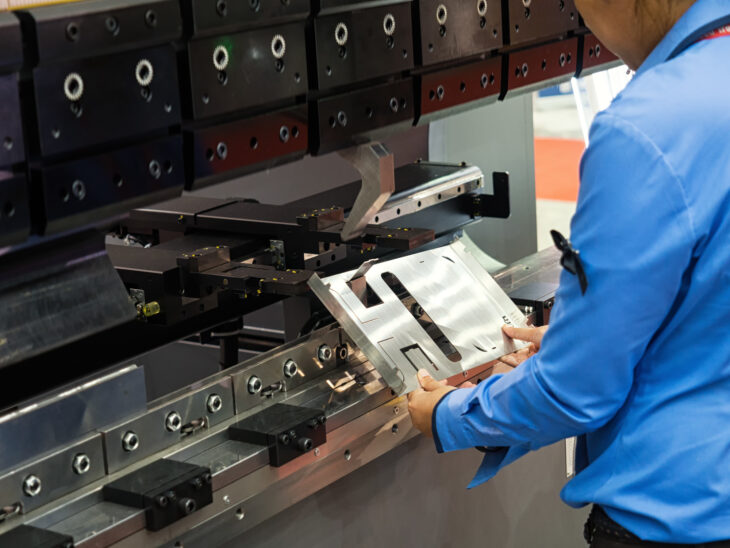

Source: prototechasia
Vacuum Casting
This is a rapid prototyping technique for the production of low volume functional plastic parts or the first-run production of plastic parts.
Rapid Tooling
This type of manufacturing uses injection molding to provide a flexible and reliable option for low volume manufacturing. The injection molded parts can be used both for full functions, fit testing, and various marketing purposes.
Sheet Metal Prototyping
This is done by bending, stamping, cutting, spinning, punching, or welding standard gauge metal to make a one-off or few prototypes for initial testing.
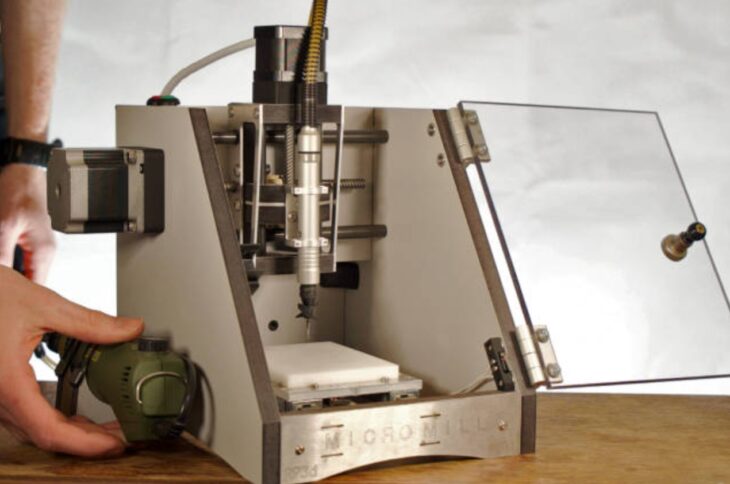

Source: Electronics Weekly
Metal Casting Prototyping
This involves aluminum, zinc, or magnesium die casting as well as brass and steel investment casting. There is also pressure die casting which is very similar to injection molding.
Conclusion
Low volume manufacturing is of great use and plays a vital role in the rapid prototyping industry. Choosing among the different types of its techniques to use is determined by the availability of materials, tools, and also the desired product required, cutting down all costs in the rapid prototyping industry.
