In the world of digital product design, two terms often used interchangeably are UX and UI design. However, they represent distinct yet interconnected disciplines. This beginner’s guide aims to shed light on the difference between UX and UI design, their unique roles in creating exceptional user experiences, and how they work together to craft successful digital products. The guide was prepared by the specialists of Outcrowd branding agency https://www.outcrowd.io/design-page .
Contents

Source: outwitly.com
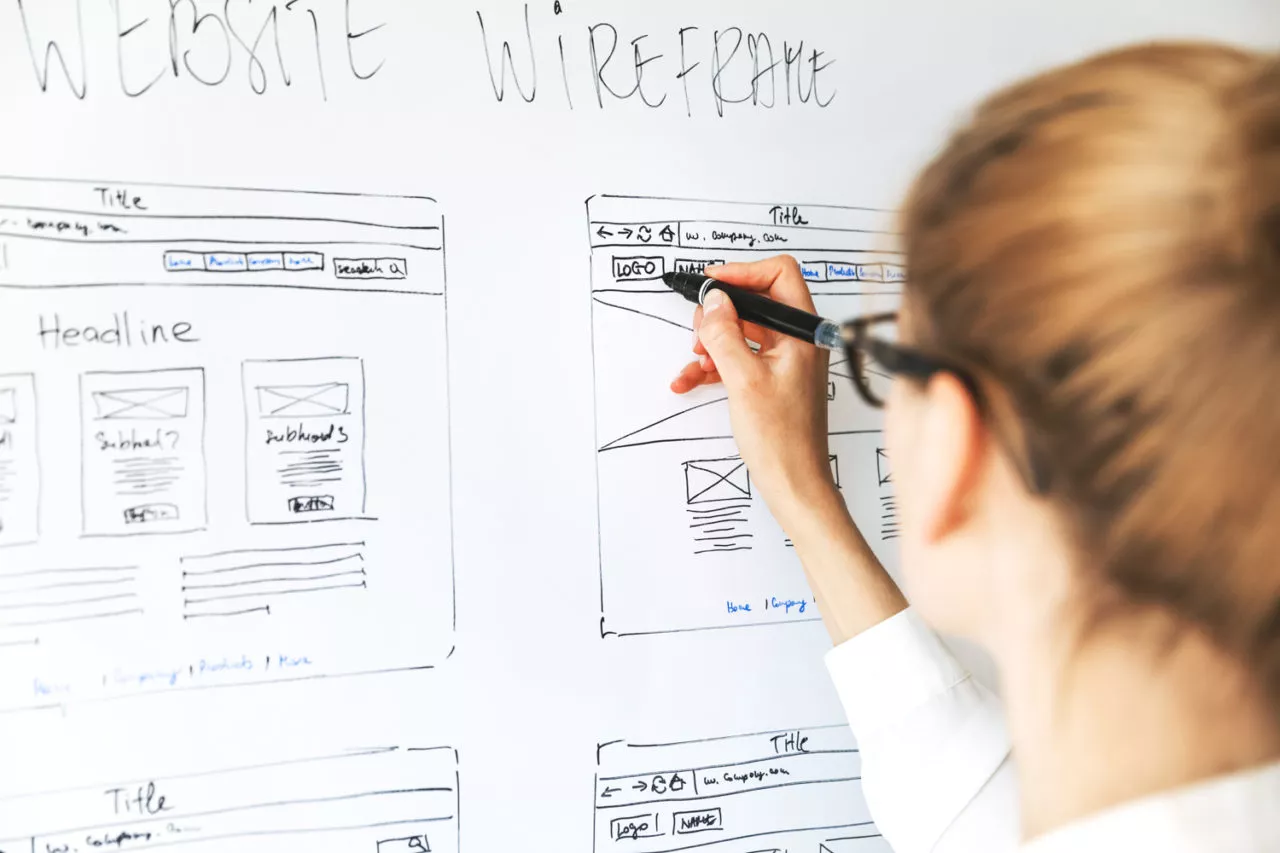
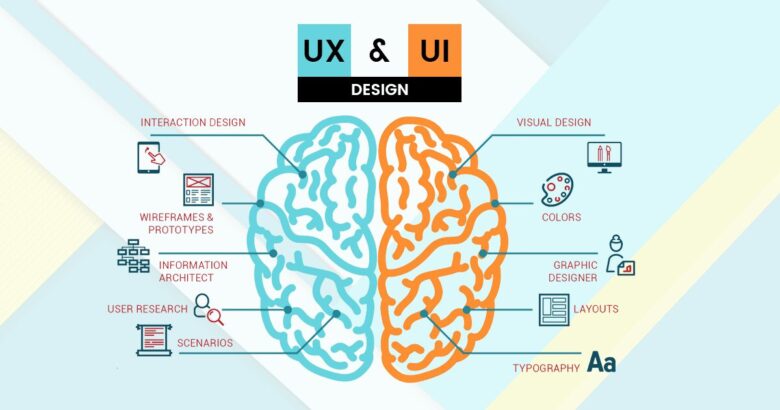
At its essence, User Experience (UX) design revolves around crafting user-centered interactions that are intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable. It encompasses the entire journey users undertake while interacting with a product, service, or platform. From the moment a user encounters a digital interface to the final interaction, UX design orchestrates every touchpoint to deliver a seamless and delightful experience. Key tenets of UX design include:
- User Research and Analysis: Understanding users’ needs, preferences, behaviors, and pain points through research informs the design process, ensuring solutions cater to actual user requirements.
- Information Architecture: Organizing content and functionality in a structured manner, ensuring users can easily find what they seek without confusion.
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Creating wireframes and prototypes helps visualize the user journey and interactions early in the design process, allowing for iteration and refinement.
- Usability Testing: Conducting usability tests with real users uncovers insights into the effectiveness of the design, identifying areas for improvement.
- Seamless Interaction: Designing interactions that feel natural and intuitive, guiding users through their journey effortlessly.
- User Empathy: Infusing designs with empathy by understanding users’ emotions and catering to their emotional needs.
What Is UI Design: The Art of Visual and Interactive Elements

Source: codilar.com
User Interface (UI) design revolves around the aesthetics and interactivity of a digital interface. It encompasses the visual elements—such as colors, typography, icons, and imagery—as well as the layout and arrangement of these elements to create an engaging and visually appealing experience. Key components of UI design include:
- Visual Identity: Creating a cohesive visual identity that aligns with the brand, utilizing colors, typography, and imagery to convey the brand’s personality.
- Typography and Readability: Selecting appropriate fonts and ensuring legible text size and spacing for comfortable reading.
- Iconography: Designing clear and meaningful icons that communicate actions and concepts effectively.
- Layout and Composition: Arranging UI elements in a visually balanced and aesthetically pleasing manner, guiding users’ attention and interactions.
- Responsive Design: Adapting UI elements for different screen sizes and devices to ensure a consistent experience.
- Visual Hierarchy: Establishing a clear hierarchy of information to guide users’ focus and emphasize important content.
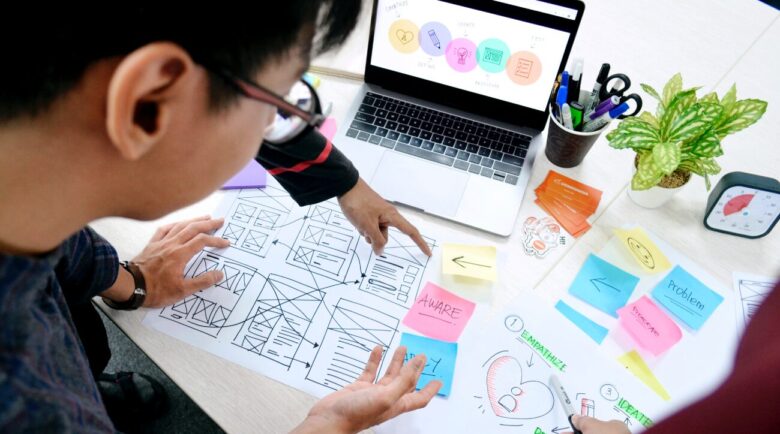
Key Differences Between UX and UI Design
Source: gst.touro.edu
1) Focus and Scope:
- UX Design: The primary focus is on the overall user experience and how users interact with the product. It includes user research, wireframing, prototyping, and usability testing to optimize the product’s functionality and flow.
- UI Design: The main focus is on the visual and interactive elements. UI designers work on creating the look and feel of the product, incorporating brand elements and designing pixel-perfect interfaces.
2) User-Centric vs. Visual-Centric:
- UX Design: It is entirely user-centric, aiming to meet the needs and preferences of the target audience and ensuring a seamless experience.
- UI Design: While considering user needs, UI design is more visual-centric, aiming to make the product visually appealing and engaging for users.
3) Skill Set:
- UX Design: Requires skills in research, empathy, user behavior analysis, information architecture, and usability testing.
- UI Design: Requires skills in graphic design, visual communication, typography, color theory, and interface design.
4) Information vs. Presentation:
- UX Design: Focuses on organizing and presenting information in a user-friendly manner, simplifying complex processes, and reducing cognitive load.
- UI Design: Concentrates on presenting the information in an aesthetically pleasing and visually coherent manner, enhancing the overall look of the product.
UX and UI Design Together. How Does It Work

Source: simplilearn.com
In the intricate dance of creating digital interfaces that captivate and engage users, User Experience (UX) design and User Interface (UI) design form a dynamic partnership that fuels the evolution of exceptional user-centric experiences. This section dives deeper into the symbiotic relationship between UX and UI design, highlighting the intricacies of their collaboration and the collective impact they have on shaping the digital landscape.
The Unified Journey of User-Centered Design
- Shared Goals and Objectives: UX and UI designers share a common mission—to create interfaces that seamlessly address user needs, foster usability, and deliver aesthetic appeal.
- Early Collaboration: The collaboration begins at the conceptualization stage. UX designers establish the blueprint of the user journey, defining the structure, functionality, and flow of the interface. UI designers, in turn, translate this framework into visually compelling elements.
Visualizing the Narrative: The Role of UI Design
- Bridging Emotion and Interaction: UI designers bring the narrative crafted by UX designers to life through visual elements. Colors, typography, icons, and imagery collectively convey emotions, guide interactions, and align with the brand’s identity.
- Visual Hierarchy and Storytelling: UI design strategically employs visual hierarchy to guide users through the interface. By prioritizing elements and content, designers tell a visual story that leads users along a seamless journey.
Functionality and Form: The Confluence of UX and UI
- Functional Aesthetics: The union of UX and UI design ensures that aesthetics are not just superficial; they are deeply connected to functionality. Visual elements are designed with purpose, aiding usability and enhancing the user experience.
- Responsive Design: The symbiotic relationship extends to responsive design, where UI elements are adapted for various screen sizes and devices to maintain consistency and usability.

Source: crazyegg.com
Iterative Refinement: Nurturing Growth and Excellence
- Continuous Feedback Loop: Throughout the design process, UX and UI designers collaborate closely, exchanging insights, ideas, and feedback. This iterative approach fosters improvements and refinements that enhance the final product.
- Usability Testing and UI Optimization: UX testing provides UI designers with valuable data to refine the visual aspects of the design, ensuring that both the structure and aesthetics contribute to a seamless experience.
The Impact on Branding and Perception
- Consistent Branding: The symbiosis of UX and UI design enforces consistent branding. Visual elements resonate with the brand’s identity, reinforcing its essence and fostering brand recognition.
- Emotional Connection: A harmonious UX and UI design generates emotional connections with users. Engaging visuals combined with intuitive functionality create experiences that resonate on both practical and emotional levels.
Crafting Lasting Impressions: The Legacy of UX and UI Design
- User Loyalty and Advocacy: A well-executed partnership between UX and UI design cultivates user loyalty. When users consistently enjoy seamless interactions and visually appealing interfaces, they are more likely to become advocates for the brand.
- Memorable Encounters: The culmination of the UX and UI partnership is an encounter that leaves an indelible mark on users. This encounter extends beyond the screen, shaping users’ perceptions, influencing decisions, and sparking lasting engagement.

Source: applify.com
Conclusion:
In conclusion, UX and UI design are two interconnected disciplines that play vital roles in creating successful digital products. UX design focuses on the overall user experience, ensuring that the product meets user needs and expectations. On the other hand, UI design deals with the visual and interactive elements, making the product visually appealing and engaging. By working together, UX and UI designers can craft seamless and delightful user experiences that set a product apart in a competitive digital landscape.
