A penetration test, commonly referred to as a pen test, simulates a cyberattack on your system to look for weaknesses that might be exploited. Penetration testing is frequently used to enhance a web application firewall and improve its security.
In pen testing, various application systems are breached in an effort to find security holes:
- front-end and backend servers;
- APIs, and others.
Unsanitized inputs are vulnerable to code injection attacks ‒ this is why pen testing exists.
You can improve your web application protocol security settings and fix found vulnerabilities using the information derived from the penetration test.
Contents
How does it work? What do you pay for?

Source: clearnetwork.com
A few significant factors decide how much will the penetration test cost for your web project. Let’s review the most prominent of them, according to the cost factors in company h-x.technology.
Goals
What you want to achieve will determine how much the penetration test will cost.
The cost will vary greatly depending on whether you want to test the physical access of a small business, a service with several servers across the globe, or any combination of networks, apps, and devices. Or perhaps you want to assess how resistant your company is to social engineering attempts.
Each goal affects the price as different approaches will be used.
Once it concerns the testing environment, size will also be a matter. Also, the type of testing used will also affect the price. Maybe, you will want to ask for a “blind” penetration test or the opposite ‒ give the testing team as much information as possible.
Workload
This has to do with how much time the testing team will require to complete the penetration test. The quantity of users, systems, IPs, apps and facilities involved strongly influences the price and duration of the test.
It will take longer to test a single IP with a sizable consumer-oriented web portal and many different account types than a few hundred IPs that you simply have to ping in order to perform a test.
If there are any technical restrictions built into the system, it might require more time to perform testing ‒ hence the higher price.
Testing methods

Source: cyberark.com
Usually, testers have different approaches to offer.
For example, there are entry-level tests — they are automated and designed to search through code in order to discover vulnerabilities.
A more sophisticated and practical approach for pen testing is set to discover vulnerable access points and the chances they can be exploited. After these are found, the testing team defines the most vulnerable spots that need remediation.
The far more thorough and expensive pen-testing strategy looks for and exploits access points. Still, it also seeks to take advantage of those flaws to discover what more the potential attacker could be able to accomplish. This type of testing is more thorough than a simple vulnerability assessment and aids your business in understanding the levels of risk and prioritizing the best remediation practices.
Expertise
It is only logical that you might pay more for services performed by a team with more expertise, just like it works with any other service. It is advised to spend money on a testing team that has experience doing successful tests and has vast knowledge about your industry.
Re-testing
The main purpose of every penetration test is to find weaknesses in the system. Re-testing will be necessary to check whether these weaknesses in your systems and apps have been fixed.
It is crucial to take into account how the expense of remediation re-testing will affect the project’s total budget.
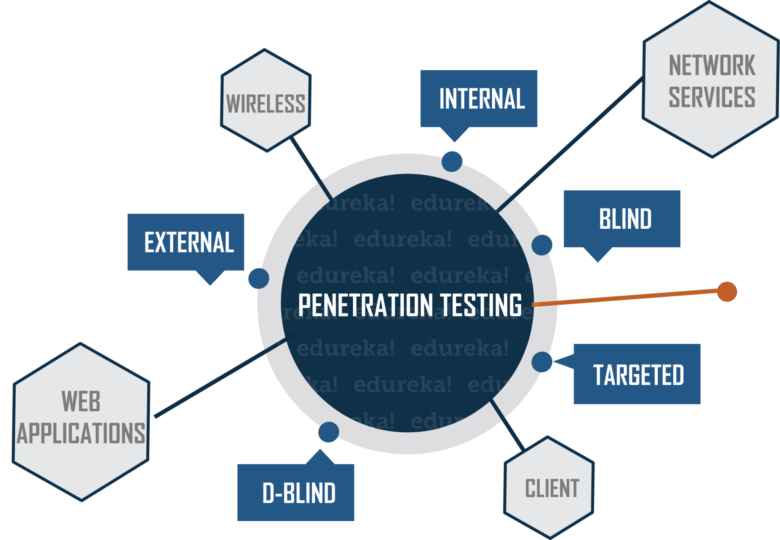
Types of Penetration Testing
Source: binsec.tech
Depending on an organization’s information security needs, there are various types of penetration testing that can be employed.
• External Penetration Test: This type of pentest focuses on external elements of the network such as external-facing servers, firewalls, web servers, and other perimeter devices. This test assesses network vulnerabilities from outside the network.
• Internal Penetration Test: An internal penetration test focuses on internal elements such as internal subnets, user accounts, policies, etc., while also looking at any connections between Internal systems and external facing services. The scope of this test is within a perimeter established by the organization that includes both private IT landscapes as well as public-facing components.
• Web Application Penetration Test: This type of penetration test examines web-based applications hosted within Internal Infrastructure or on a third-party service provider in order to check for security flaws from both known and unknown sources. Typical goals include discovering weaknesses related to authentication mechanisms, input validation errors, or authorization issues.
• Wireless Pentest: A Wireless Pentest checks for wireless vulnerabilities created by wireless access points (WAP). This pentest entails the use of special equipment for analyzing signals sent over various wireless networks in order to detect any gaps in used protocols or other weak points that may allow unauthorized access into a system or allow eavesdropping of data sent from one system to another through traffic analysis techniques.
• Mobile Application Testing: Mobile application penetration testing looks for weaknesses caused by modified code libraries within mobile applications and how they interact with user data such as location services, passwords, and access rights granted by users to distributed applications while interacting with the host OS (eg iOS/Android). It is important to assess the security measures taken by developers when designing mobile apps; however complex this may seem it is still possible to conduct due diligence processes against existing mobile codebases in order to identify potential risks before they reach the production release stage.
More complex approaches

Source: packetlabs.net
The broad applicability of penetration testing across businesses and security frameworks is its biggest asset. The following are four of the most advanced, most effective testing strategies:
- network-focused testing;
- independent testing of the web application;
- social engineering attacks simulation;
- running tests on different physical assets.
Apart from these more sophisticated penetration testing approaches, more basic measures can also provide insightful results. As it was said earlier, it all depends on your testing objectives and the complexity of your project.
How much does it cost?
As you can see, the price heavily depends on the workload, testing objectives, and technologies that must be implemented. The smaller your business, the less expensive the penetration test will be. Price lists for advanced IT systems with complex architecture can reach hundreds of thousands of dollars.
