Follicular unit extraction or FUE is one of two major surgical hair restoration methods and the most convenient. The other technique goes by the name of follicular unit transplantation and marks the beginnings of the modest hair transplantation days. Owing to its inconvenience and side effects, FUT is what motivated the invention of FUE. Below we will discuss how both techniques work and how they differ.
Contents
Follicular unit transplantation (FUT)
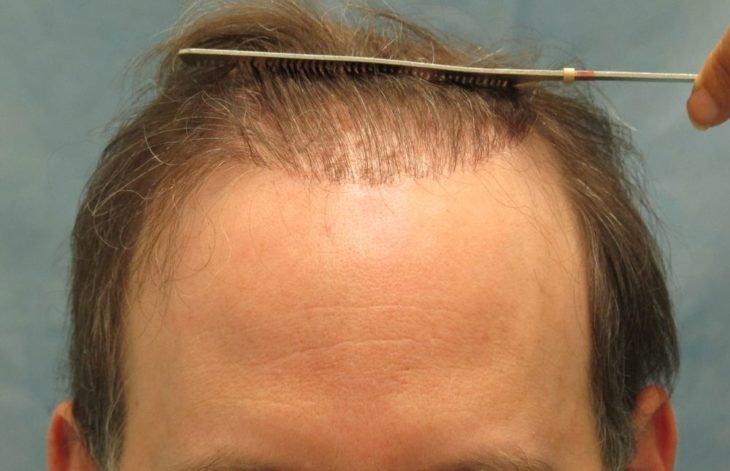
The process overview of FUT hair transplants involves extraction of follicular units (grafts), preservation of grafts, channel-opening on recipient site, and finally implantation of grafts. The method of graft extraction in FUT is what breeds all the issues. To harvest grafts, an entire strip of the scalp has to be excised, the donor area is then stitched and the strip is dissected. [1] [2]
Img source: hairlosstalk.com
This results first and foremost in a visible linear scar on the donor site that often limits that patient’s choice of hairstyles in the future. In addition, the method of excision poses a risk of nerve damage in the area that can either be temporary or permanent. In some instances, patients experience numbness for at least six months after the surgery.
You can find out more about hair transplants at vera clinic
Follicular unit extraction (FUE)
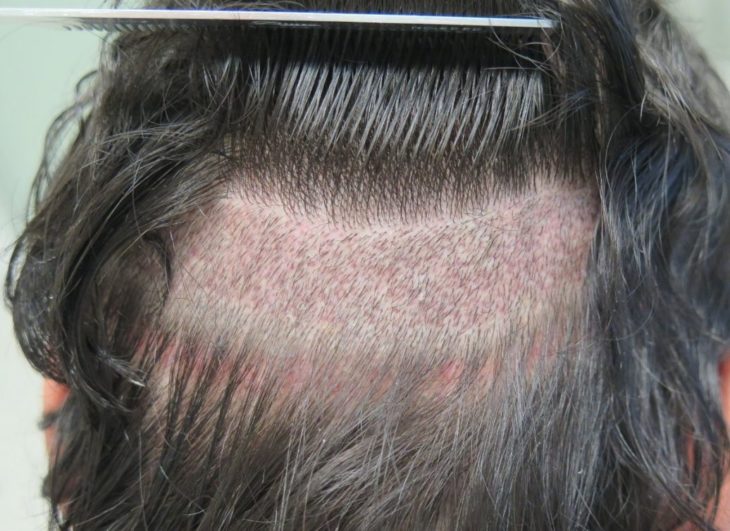
The method of follicular unit extraction follows a similar procedure to FUT. Starting with extraction, followed by preservation of grafts and channel opening and ending with implantation. However, the harvesting phase differs in FUE. Instead of excising an entire strip of skin, surgeons employ a micro-punch that isolates follicular units through creating circular incisions around the follicular unit. Later, with the help of a forceps, the graft is harvested.
Img source: fuehairtransplantclinics.co.uk
This method of individual extraction leaves behind microscopic scars that are not visible with the naked eye. The nature of the FUE procedure eliminates risks such as nerve damage.
Applications of FUE and FUT
FUT and FUE are both hair restoration techniques, however, given the difference in the extraction phase their applications vary with FUE being more versatile. Hair transplants are not limited to scalp hair, facial hair and body hair are all included. Since body parts like the eyebrows or the beard require donor hair that is similar in structure to that of the target area, FUT hair transplants are not effective. On the other hand, FUE makes it possible to extract hair from the body without leaving linear scars.
In summary
Follicular unit extraction (FUE) and follicular unit transplantation (FUT) are the only two major techniques of hair transplantation. The remaining techniques of hair transplantation are variants of FUE. In essence, the two techniques differ mainly in the extraction step where FUT follows a more invasive method that leaves a linear scar and could cause nerve damage. On the other hand, FUE is more immaculate owing to its method of harvesting where follicular units are individually extracted leaving behind minuscule scars.
Although the difference is mainly in one phase and may seem trivial, it is actually the secret to why one technique is more successful than the other and why FUE has more versatile applications in comparison to FUT.
