Every home requires a protective shield against nature’s elements, and that’s where a roof steps in. But beyond just shelter, a roof plays a pivotal role in maintaining a home’s structural integrity and indoor comfort. Central to this is the concept of roof ventilation. In this deep dive, we uncover the intricacies, benefits, and technological marvels of roofing ventilation systems. Let’s embark on this enlightening journey.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Roof Ventilation
- 2. Different Types of Roof Ventilation Systems
- 3. The Science Behind Roof Ventilation
- 4. Benefits of Proper Roof Ventilation
- 5. Calculating Ventilation Requirements
- 6. Common Ventilation Problems and Solutions
- 7. Innovations in Roof Ventilation Technology
- 8. DIY vs. Professional Installation
- 9. Environmental Impact of Roof Ventilation
1. Understanding Roof Ventilation

Source: greenhomeinstallations.org
Roof ventilation goes beyond the basic concept of letting air in and out. At its core, it’s a system intricately designed to optimize airflow, ensuring temperature regulation, moisture minimization, and the enhancement of the roof’s lifespan. Neglecting this can lead to highly visible and problematic outcomes—rapid mold growth, beams that become warped due to retained moisture, and a steep rise in energy bills due to poor insulation. Furthermore, for those seeking a comfortable home environment, the difference a well-ventilated roof makes is undeniable. It ensures a consistent circulation of air, adeptly balancing the internal temperatures, making homes cozy during winter and refreshingly cool in summer.
2. Different Types of Roof Ventilation Systems
The world of roofing presents a rich tapestry of ventilation options, tailored to cater to the diverse needs of homeowners:
Ridge Vents: Seamlessly blending with the roof’s design, these discreet vents, positioned at the roof’s peak, are particularly ideal for homes that boast a regular-shaped roof. Their design is optimized to ensure the effective expulsion of hot air.
Soffit Vents: Installed right under the eaves, these vents play a pivotal role. They’re the backbone of the ventilation system, allowing cooler, fresh air to permeate the attic. This works in harmony with other systems like ridge and gable vents to create an efficient circulation.
Gable Vents: While capable of standalone operation, these vents, strategically located on the roof’s gable end, often work in tandem with other systems. Their design capitalizes on the wind, using it as a natural mechanism to drive out hot air.
Turbine Vents: Particularly fascinating in design, these wind-driven vents excel at drawing out warmer air. For homes situated in regions with a consistent wind pattern, they’re a boon.
The key to leveraging these systems effectively lies in understanding both the architectural nuances of one’s home and the intricacies of the local climate.
3. The Science Behind Roof Ventilation
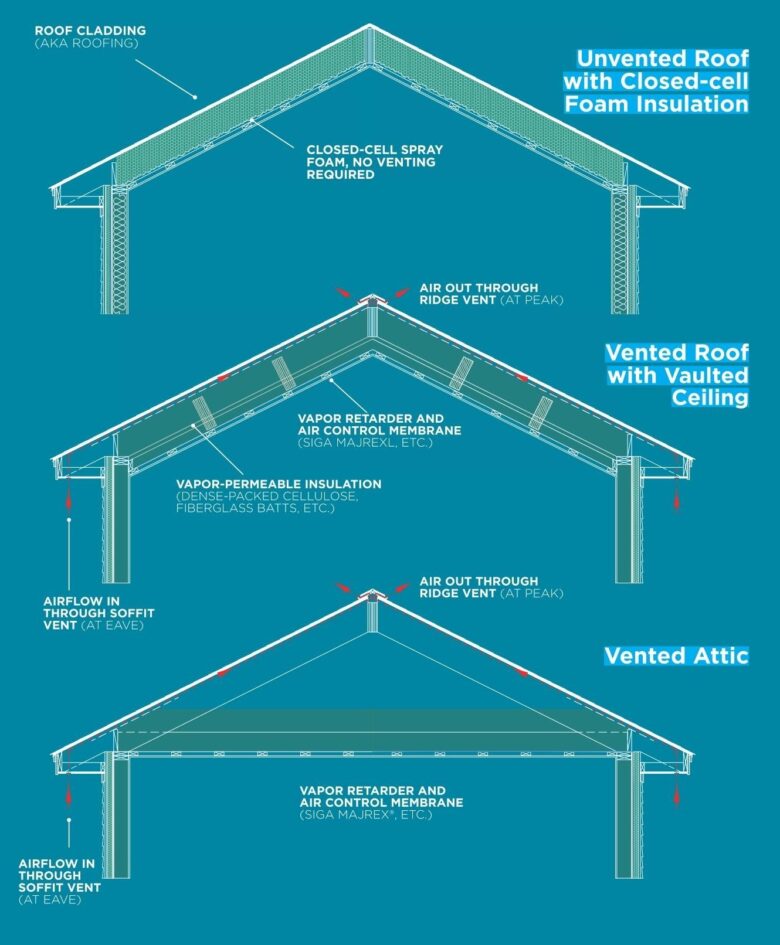
Source: greenmainehomes.com
Behind the seemingly simple process of roof ventilation lie compelling scientific principles:
The Stack Effect: When warm air rises, it tends to accumulate at the highest point in a confined space. This natural phenomenon induces a pressure differential. Consequently, this pushes the hot, stagnant air out, making room for the cooler air to be drawn in.
The Wind Effect: Wind plays a pivotal role in the ventilation process. As it collides with the roof, it significantly accelerates air exchange, pushing the hot air out, while further strengthening the natural ventilation process.
Grasping these fundamental dynamics is essential for anyone looking to design or implement an effective and efficient roof ventilation system.
4. Benefits of Proper Roof Ventilation
Having a meticulously planned and executed ventilation system brings a plethora of benefits:
Extended Roof Lifespan: Effective ventilation means moisture finds no haven. This, in turn, ensures that roofing materials stay robust, free from decay, and the often devastating impact of long-term moisture exposure. This means less roof repair adventures for you.
Reduced Energy Costs: With an attic that maintains a consistent cool temperature, homeowners will find their air conditioning systems working far less, leading to tangible energy savings.
Mold and Moisture Prevention: A continuous flow of fresh air ensures no stagnation, and more importantly, reduces condensation. Less condensation means mold finds no breeding ground, ensuring healthier living spaces.
Improved Air Quality: Homes with excellent ventilation constantly replenish indoor air. This means the stale air, which often carries pollutants and allergens, is frequently replaced, fostering a healthier living environment.
5. Calculating Ventilation Requirements

Source: thoughtco.com
Assessing and determining the right amount of ventilation isn’t just an architectural exercise—it’s a blend of art and precision. To create a comfortable living environment and ensure the longevity of roofing materials, it’s crucial to balance multiple variables:
Roof Size: Industry stalwarts have long advocated a ratio when it comes to ventilation: approximately 1 square foot of ventilation for every 300 square feet of attic space. However, this isn’t a one-size-fits-all guideline. It’s essential to consider other variables.
Attic Size and Design: The attic’s volume, combined with its unique design, plays a significant role. It helps in determining how air flows, where it might stagnate, and how best to ensure consistent circulation.
Local Climate: The climate isn’t just about the average temperatures. It’s about understanding the range of extremes. While homes in warmer climates benefit from rigorous ventilation, those in colder regions need a more balanced approach. This is essential to maintain warmth during chilly winters and to prevent ice dams.
6. Common Ventilation Problems and Solutions
Like any system exposed to natural elements, ventilation mechanisms can encounter their set of challenges:
Blockages: It’s not uncommon for vents to become blocked over time. Accumulated debris, bird nests, or even snow can severely inhibit airflow. The repercussions of this are often immediate and detrimental.
Imbalanced Systems: An intricate balance between intake systems (like soffits) and exhaust mechanisms (like ridge vents) is paramount. An imbalance can hamper optimal airflow, leading to inefficiencies.
To combat these challenges, homeowners are advised to engage in regular inspections, ensuring their vents remain clean and unobstructed. Additionally, expert consultations can offer solutions, recalibrating systems to restore optimal functionality when necessary.
7. Innovations in Roof Ventilation Technology

Source: 1stcoastmrs.com
In today’s digital age, even the traditional domain of roofing isn’t immune to technological advancements:
Smart Ventilation Systems: These aren’t your ordinary vents. Equipped with sensors, they continuously monitor external conditions, adjusting in real-time to ensure optimal airflow. This self-regulation capability ensures maximum efficiency without any manual intervention.
Solar-Powered Vents: Embodying the spirit of sustainable living, these vents are a testament to green technology. By harnessing solar power, they operate efficiently, minimizing their carbon footprint and reducing dependence on traditional power sources.
Such advancements aren’t just about enhancing functionality. They represent the broader shift towards sustainability, merging eco-consciousness with cutting-edge technology.
8. DIY vs. Professional Installation
The choice between DIY kits and professional installations often hinges on multiple factors:
Expertise: There’s no denying the value professionals bring. With their years of accumulated experience and knowledge, they ensure that ventilation systems are tailored and optimized to cater to each home’s unique challenges and requirements.
Safety: Vent installation, especially on sloping roofs, is fraught with risks. Professionals come equipped not just with tools, but also with training and safety gear to mitigate potential hazards.
For those who remain undeterred and wish to embrace the DIY route, it’s crucial to prioritize safety. Leveraging expert consultations and familiarizing oneself with safety protocols can ensure successful installations.
9. Environmental Impact of Roof Ventilation

Source: westpacroofing.com
Roof ventilation systems don’t just serve homes; they have broader implications:
Reduced Energy Consumption: A well-ventilated home doesn’t over-rely on artificial cooling systems. This translates to less electricity consumption and, by extension, reduced carbon emissions, benefiting the environment.
Sustainable Materials: Modern ventilation systems often incorporate materials that prioritize sustainability. Whether it’s recycled content or eco-friendly production methods, the emphasis is on reducing environmental impact.
Conclusion
Roof ventilation, though often overlooked, is a cornerstone of modern home design. It’s an amalgamation of science, design, and technology, aiming to enhance structural longevity, elevate comfort, and champion sustainability. As you ponder your next roofing decision, remember: It’s not just about covering your home; it’s about letting it breathe.
