In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, the smooth flow of information is vital. This is where industrial wireless communications step in. Basically, industrial wireless communications are the backbone of modern industrial settings, revolutionizing how machines communicate and operate.
But if you’re looking to understand the basics of industrial wireless communications more, then this article will be your guide.
Contents
Definition of Industrial Wireless Communications
At its core, industrial wireless communications refers to wireless technologies in industrial settings. This means devices and machines in factories and plants can communicate without physical cables, like those used in traditional wired systems.
This technology is crucial in a factory floor buzzing with activity, where machines, sensors, and devices exchange information. Industrial wireless communications offer a dynamic and flexible solution to connect the components of a modern industrial ecosystem.
Wireless technology utilizes radio waves or infrared signals to transmit data, unlike wired setups that rely on physical connections. This eliminates the constraints of cables, offering greater flexibility in device placement.
Key Components of Wireless Systems
Understanding the key components of these systems is vital. Industrial wireless systems consist of transmitters and receivers capable of sending and receiving signals. These devices communicate through wireless protocols, the rules governing their interaction.
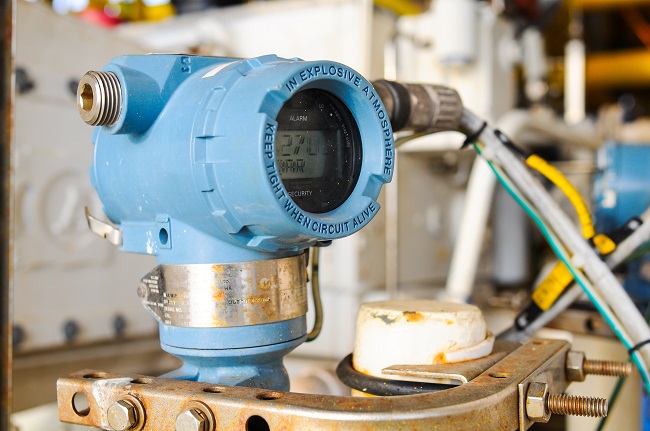

Source: processindustryforum.com
Transmitters
Transmitters are devices responsible for sending signals wirelessly. In industrial wireless communications, transmitters are often sensors or control systems that gather and transmit data or commands to receivers.
Receivers
Receivers capture and interpret the transmitted signals. Industrial receivers are commonly integrated into machinery, control systems, or monitoring devices. They are crucial in receiving information from transmitters.
Wireless Protocols
Wireless protocols are sets of rules governing how devices communicate wirelessly. They ensure standardized communication, allowing different devices to understand and interpret signals correctly. Common protocols include:

Source: pcmag.com
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi, a term familiar to anyone connected to the internet wirelessly, also finds its place in industrial settings. It allows devices to connect to a local network wirelessly, providing a reliable and fast means of communication within a defined range.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth, known for connecting our headphones and smartphones, also plays a significant role in industrial communication. Its short-range connectivity is valuable for devices that need to exchange information in close proximity.
Zigbee
Zigbee is a low-power, short-range communication protocol ideal for industrial sensor networks. It excels in applications where devices must operate on minimal power for extended periods.
LoRa
LoRa (Long Range) is designed for applications that require long-range communication with low power consumption. This makes it suitable for industrial scenarios where devices are spread over large areas.
Applications and Suitability in Industrial Settings
The choice of protocol depends on the specific needs of an industrial application. Wi-Fi might be suitable for high-speed data transfer, while Zigbee and LoRa might be preferred for low-power, wide-area applications.

Source: iebmedia.com
Wireless Sensors in Industrial Environments
Sensors act as the eyes and ears of industrial processes. In an industrial wireless communication setup, these sensors wirelessly transmit crucial data about temperature, pressure, humidity, and more, enabling real-time monitoring.
Advantages of Wireless Sensor Networks
Going for wireless sensor networks offers several advantages. They eliminate the need for complex wiring, reduce installation costs, and provide the flexibility to adapt to changing industrial layouts.
Benefits of Industrial Wireless Communications
In industrial operations, the adoption of wireless communication brings many advantages, making the way for enhanced efficiency and adaptability. Besides that, here are the main benefits of wireless communication in an industrial setting:

Source: forcetechnology.com
Increased Flexibility and Mobility
Wireless communication liberates devices from the shackles of physical connections. Machines can be repositioned, and new equipment integrated without the constraints of cables, allowing for unparalleled flexibility and mobility.
Cost Savings and Reduced Installation Time
Traditional wired setups demand extensive cabling, leading to higher installation costs and longer setup times. Industrial wireless communication streamlines this process, reducing both time and expenses.
Enhanced Scalability
As industrial operations grow, so does the need for communication. Wireless systems are inherently scalable, easily accommodating new devices and expanding the communication network.
Improved Reliability and Redundancy
Wireless communication ensures a reliable and redundant network. In case one communication path is disrupted, devices can seamlessly switch to an alternative path, maintaining continuous operations.
Challenges and Solutions
While the advantages of industrial wireless communications are vast, it’s important to be aware of the challenges of this technological shift; here are some of them:

Source: tweakyourbiz.com
Security Concerns in Wireless Networks
The convenience of wireless communication brings with it concerns about security. Encrypting data and implementing authentication measures are essential to safeguard industrial networks from unauthorized access.
Interference and Signal Strength
Interference from other devices or physical obstacles can affect signal strength. Mitigating this challenge involves strategic placement of devices, signal-boosting technologies, and careful frequency management.
Standards and Interoperability
Adherence to standards and interoperability ensures seamless communication across devices from different manufacturers. Establishing common protocols allows devices to speak the same language.
Ensuring Compatibility Across Devices
In the industrial landscape, devices come from various manufacturers. Ensuring compatibility requires a commitment to standardized communication protocols, fostering a collaborative and interconnected ecosystem.
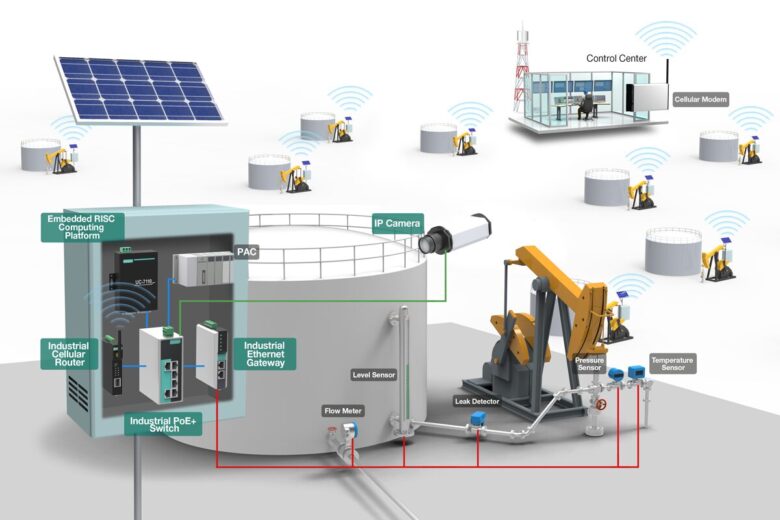
Source: pages.moxa.com
Industrial IoT and Wireless Connectivity
The Industrial Internet of Things, or IIoT, represents the integration of wireless communication with industrial processes. It involves connecting devices, machines, and systems to collect and exchange data, fostering intelligent decision-making.
The coordination between industrial wireless communications and IIoT is evident. Wireless sensors and communication protocols form the backbone of IIoT, providing the connectivity needed for a seamless flow of data.
Wireless Communication is the Future
This technology is now the foundation of modern industrial connectivity. Understanding these fundamentals is beneficial and essential for industries looking to stay competitive. As industries continue to evolve, the importance of a robust and adaptable communication infrastructure cannot be overstated.
