Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease or an IBD. It causes chronic inflammation of the digestive tract which leads to all sorts of uncomfortable problems such as severe diarrhea, weight loss, and severe abdominal pain. There are no rules as to which part of the digestive tract is affected as it differs from person to person. Living with Crohn’s disease can certainly be overwhelming and even though there is no cure for it, some treatments that can make life easier do exist. Crohn’s disease can test both your physical and emotional endurance, but with time, new habits and treatments will help you lead a happy and fulfilled life.
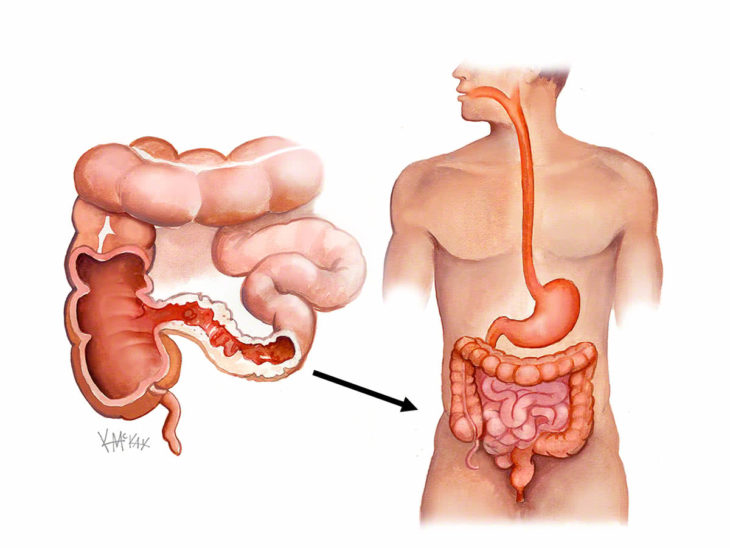
Source: Colorectal Surgeons Sydney
Causes
Many theories about what causes Crohn’s disease exist, but none of them have yet been proven. However, based on what we do know about Crohn’s disease, it’s clear that it’s caused by a combination of immune system problems, genetics, and even environmental factors. That means that other then your DNA and immune system, your daily habits can also help you develop this disease.
Up to 20 percent of people with Crohn’s disease have a parent, child, or a sibling with the same disease.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Crohn’s disease are numerous, they aren’t at all pleasant, and it takes some time to learn to live with them. Symptoms may vary from person to person depending on which area of the digestive tract is affected.
Inflammation causes severe pain in the abdomen and it will most often be felt at the lower-right side. Also, gut and mouth ulcers may appear. Ulcers are areas in the gut that may start to bleed so patients often start noticing blood in their stools.
Diarrhea is another common symptom and it can range from mild to severe. As patients often experience loss of appetite and fatigue, weight loss is almost inevitable. Loss of blood can also eventually lead to anemia.
Skin rash, uveitis, arthritis, liver and bile inflammation, and delayed growth in children can also appear and aren’t uncommon for Crohn’s disease. Some women may also find that their menstrual cycle is becoming irregular or is missing altogether.
Source: Dr. Weil
Treatment
While there is no cure for this disease yet, certain treatments may help control the inflammation, correct nutritional problems, and relieve the symptoms. Of course, the treatments differ depending on which area of the tract if affected, the severity of the disease, and the patient’s potential response to previous treatment.
Often people will go for years without experiencing any symptom and that is called remission. Unfortunately, it’s just a matter of time before the symptoms come back.
Treatments include medication, nutritional supplements, and surgery. Entyvio is an often-used prescription medication. According to experts at Healthline, this is a biologic pill that comes from the group of integrin receptor antagonists.
Some common medications also include sulfasalazine and mesalamine, but they also come with certain side effects such as nausea, vomiting, headaches, and heartburn. If a patient isn’t responding well to sulfasalazine, the doctor might prescribe other medications such as olsalazine, balsalazide, or mesalamine.
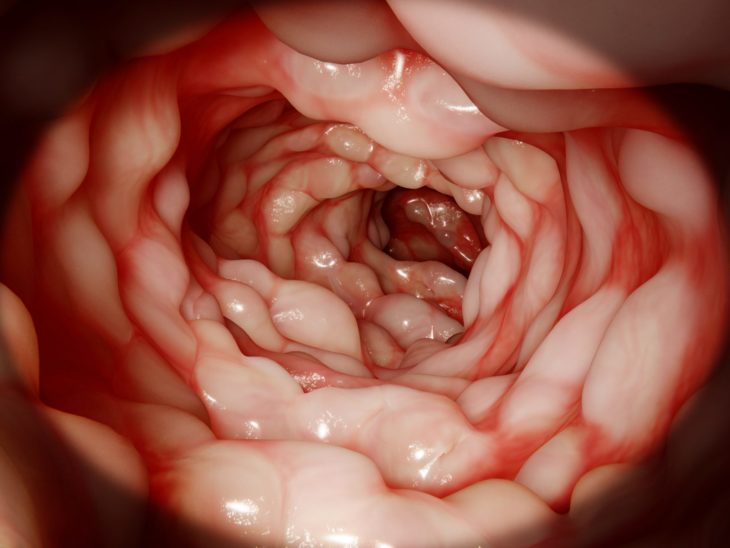
Source: INX Medical
Some antibiotics such as ampicillin, sulfonamide, or metronidazole may also be prescribed as fistulas and strictures may cause bacterial overgrowth.
