Have you ever wondered who came up with some of the most famous inventions? Looking to the past, we can find some of the most influential inventors in history. From Thomas Edison to Elon Musk, read on and discover why these inventors have left their mark on the world.
Contents
- Thomas Edison: The Father of Invention
- Nikola Tesla: The Inventor of Alternating Current
- Alexander Graham Bell: The Father of the Telephone
- Henry Ford: The Father of Automobiles
- Steve Jobs: The Father of the Digital Revolution
- Elon Musk: The 21st-Century Innovator
- Albert Einstein
- Marie Curie
- Guglielmo Marconi
- Benjamin Franklin
- Alexander Fleming
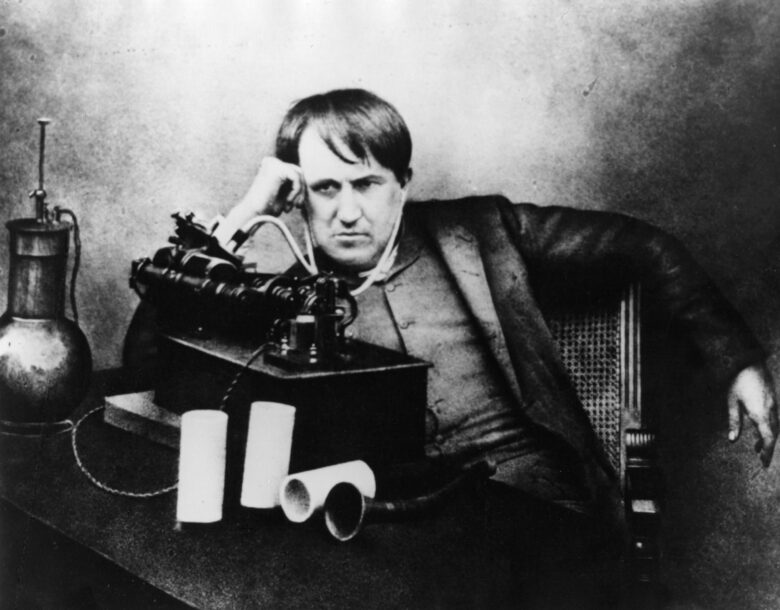
Thomas Edison: The Father of Invention

Source: biography.com
After studying science and engineering, Edison developed the incandescent light bulb and founded General Electric which has since become one of America’s largest companies. His inventions have had a considerable impact on our world today — from phonographs, motion pictures, alkaline storage batteries, stock tickers, and more — Edison is seen as the Father of Invention for his revolutionary ideas and products that changed our world for the better. In addition to these accomplishments, Edison held 1,093 patents including many related to electrical power generation and distribution. It’s clear that Edison’s contributions to the world of innovation have left a lasting impression, and companies like InventHelp strive to continue their legacy by helping inventors bring their ideas to life.
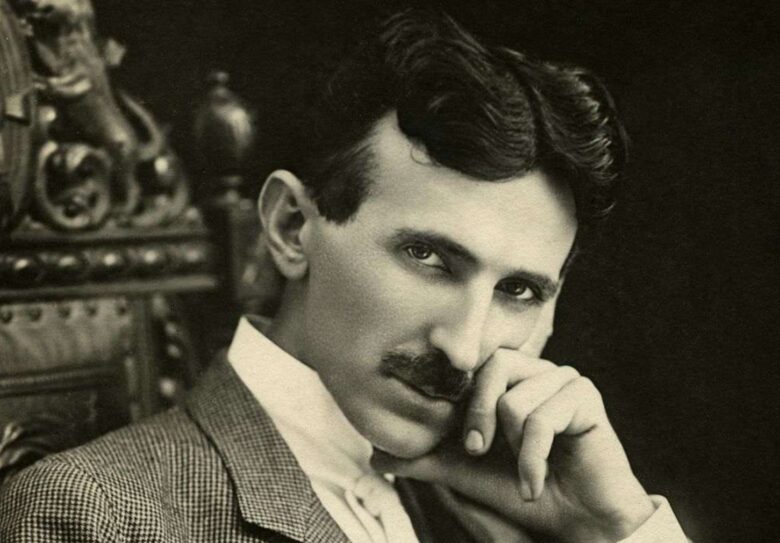
Nikola Tesla: The Inventor of Alternating Current

Source: triesteallnews.it
Nikola Tesla was a genius inventor of the 19th century who significantly contributed to the development of electricity and robotics. His inventions include alternating current power systems, fluorescent lighting, one of the first remote controls, and many more. Tesla is often credited as being responsible for ushering in the age of electricity.
In 1888, he witnessed a series of electric detonations and reasoned that alternating current was potentially much safer than direct current. He went on to develop motors and power systems using both direct current and alternating current — his large-scale three-phase system continues to form the basis for most power distribution today.
He patented various improvements to motors, transformers, generators, and other components of AC electric power station apparatus — inventions that revolutionized electrical transmission systems around the world.
Tesla’s invention also helped fuel significant growth within fields such as radio technology (he developed a radio-controlled boat), wireless communication (his famous Wardenclyffe Tower project), electromagnetism (the Teslascope for broadcasting), and xrays (he discovered their presence).
Alexander Graham Bell: The Father of the Telephone
Source: history.com
Bell was a natural teacher and innovator who had an innate understanding of the science behind sound and electricity. Much of his success was due to his willingness to think outside of accepted conventions and take risks with new technology. He co-founded American Telephone & Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1885, which soon became one of America’s largest companies. Thanks to Bell’s invention, phone lines were quickly laid all over America allowing people several hundred miles apart to communicate easier than ever before.
The legacy created by Alexander Graham Bell continues today—from voice recognition software to cell phones, many of today’s modern conveniences can be credited back to his revolutionary breakthroughs. His contributions had an everlasting impact on humanity and will be remembered for generations to come.
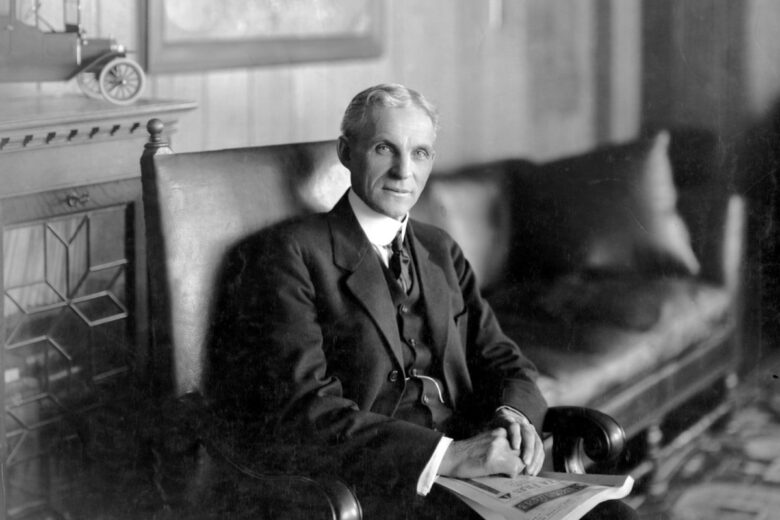
Henry Ford: The Father of Automobiles

Source: auto.howstuffworks.com
Ford was born on a farm near Dearborn, Michigan in 1863 and his interest in mechanical objects has been described as beginning at an early age. After numerous failed business ventures, Ford introduced the Model A — the first successful car to be mass-produced using an assembly line — in 1903. It was followed by several different models before ultimately introducing the Model T on October 1, 1908. The car had huge success until 1927 when it was replaced by updated models with improved designs. During this time period, Ford revolutionized communication methods between businesses with his assembly-line techniques which led to an increased demand from consumers for cars.
Ford’s influence remains prevalent today as he not only created a reliable transportation device but proposed a wage increase that allowed workers to purchase vehicles from him and thus become lifelong customers of his products which continues to influence customer loyalty today. Ford also offered unheard-of benefits for their employees including profit-sharing plans which led to company loyalty from employees who wanted to work at a place that treated them well and offered perks such as vacations and pensions.
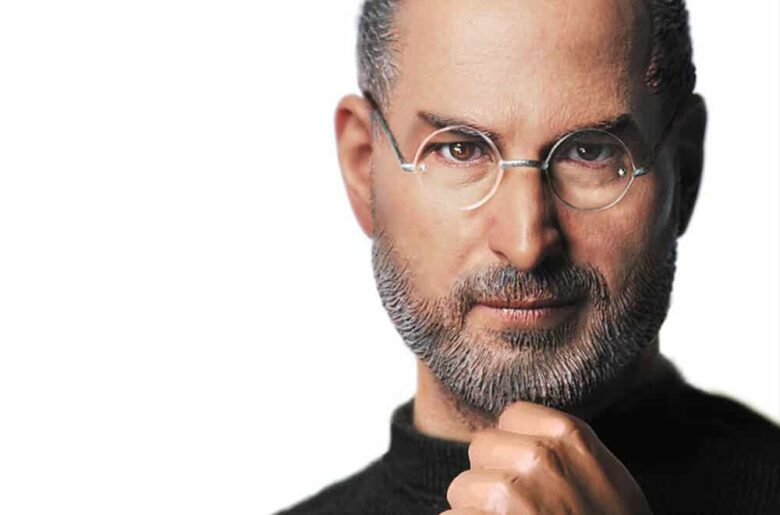
Steve Jobs: The Father of the Digital Revolution

Source: unboxingstartups.com
From high school days selling “blue boxes,” calling locations around the world; to being fired from Apple in 1985; to returning in 2006 to revive Apple from near bankruptcy; he leaves behind an unmeasurable legacy as one of history’s most influential innovators.
Steve Jobs was a master of connecting ideas, art, and science and achieved greatness at blurring the lines between them with his creations, i.e., iPad, iPhone, iTunes, etc. He had visions ahead of his time that revolutionized computing technologies in the 1980s and up until today. He was passionate about design and wanted to bring products not just any product but ones with heart and soul that are elegantly simple yet powerful; products like no other seen before or after him truly products of passion that evoked many loyal fans.
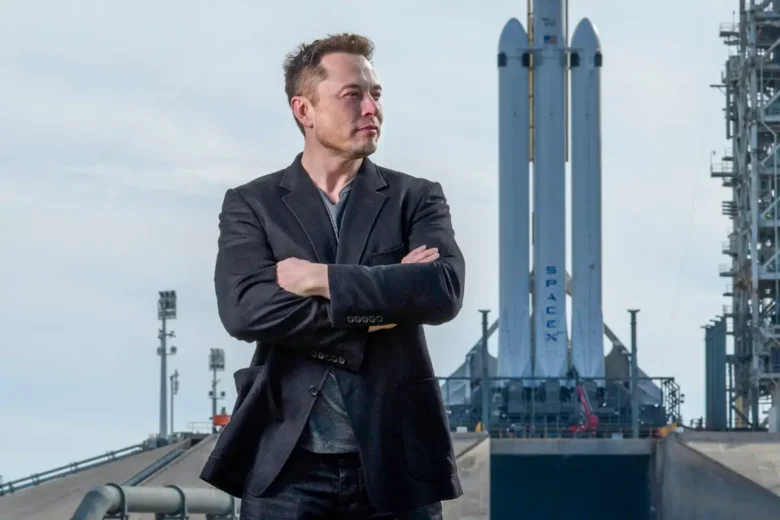
Elon Musk: The 21st-Century Innovator

Source: newscientist.com
As the co-founder, CEO, and lead designer of SpaceX, co-chairman of OpenAI, and founder, CEO, and product architect of Tesla Motors, Elon Musk embodies the spirit of innovative entrepreneurship. His ambitious endeavors have revolutionized space travel, helped make electric cars a viable option for consumers, and inspired a generation to become leading inventors in their own right.
Musk’s childhood passion for technology remained with him throughout his life. After attending university in Canada to study economics and physics, he enrolled at Stanford University to pursue a Ph.D. degree in energy physics — but left after only two days when he realized his true interests lay elsewhere. Instead of returning home to South Africa as expected, Musk settled in the United States. After multiple entrepreneurial pursuits over the span of several years — including co-founding an online financial services company called X.com (merged into PayPal) — today Musk is regarded as one of the most influential inventors in history due to his contributions to transportation and space exploration.
At SpaceX alone, Musk has tested multiple technologies such as reusability —which involves launching a single rocket multiple times —and vertical takeoff/vertical landing capabilities that optimize fuel usage during launch vehicles’ descent back to Earth. His team ultimately managed to make history when they successfully launched a reusable rocket back into space on March 30th, 2016 – an achievement that was considered nearly impossible just two decades ago. Musk’s ever-evolving resume even includes helping design powered exoskeletons for humanity’s exploration efforts on Mars– an idea he dreamed up while working tirelessly on rocket launches and electric cars back on Earth!
With precedent-breaking successes like these at his back, it’s no wonder Elon Musk has become known as “The 21st Century Innovator” – utilizing innovative technologies to shape our world for the better.
Albert Einstein

Source: newscientist.com
Albert Einstein changed the world of physics with his theory of relativity and the famous equation E=mc². This equation shows that energy and mass are interchangeable, setting the stage for nuclear energy. It also led to the creation of the atomic bomb, a weapon of mass destruction. Einstein’s work didn’t stop at physics; he also contributed to the development of quantum theory and cosmology. His theories have applications in various fields, from GPS technology to understanding the universe’s origins.
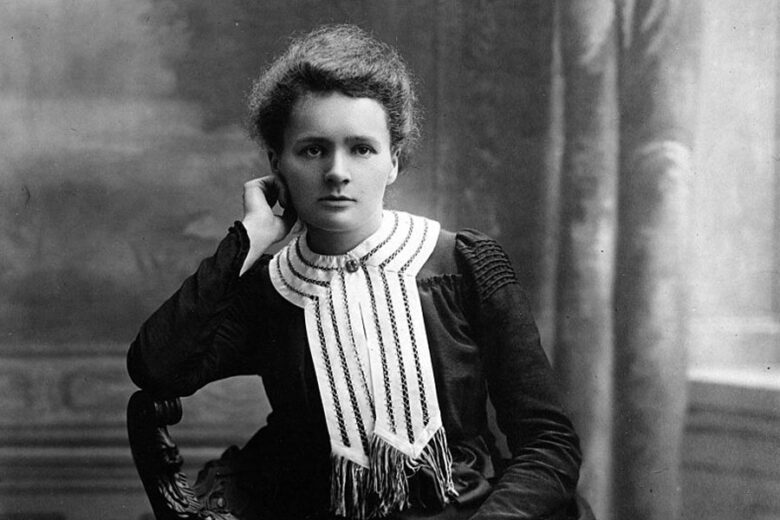
Marie Curie

Source: media.franceintheus.org
Marie Curie broke barriers in both physics and chemistry. She is best known for her research on radioactivity, a term she coined. Alongside her husband, Pierre Curie, she discovered two new elements: polonium and radium. These discoveries opened up new avenues for understanding atomic structure. More importantly, her work laid the groundwork for X-ray machines and radiation therapy in cancer treatment. Curie remains the only person to win Nobel Prizes in two different scientific fields, making her contributions invaluable. If you have even a 1% of Curie’s idea you should visit this website.
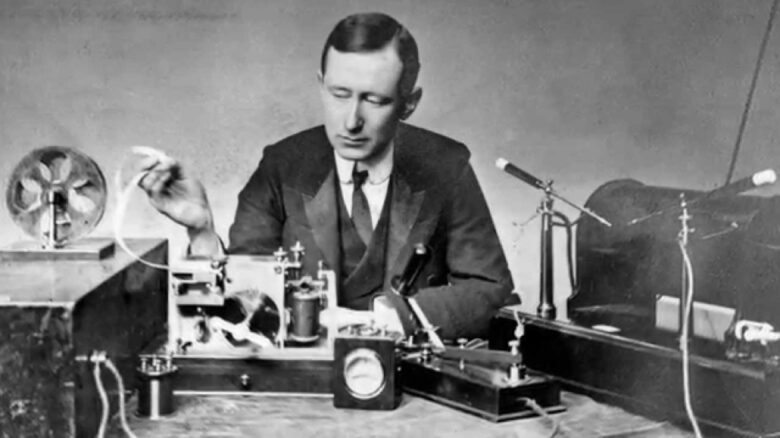
Guglielmo Marconi

Source: pioneerinstitute.org
Marconi revolutionized the way we communicate by developing the radio. He conducted experiments that proved radio waves could travel over long distances, breaking the limitations of wired communication. Marconi’s work laid the foundation for all wireless gadgets we use today, from mobile phones to Wi-Fi networks. He received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1909 for his contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy. His work set the stage for the global communications network we rely on today.
Benjamin Franklin

Source: historyoasis.com
Benjamin Franklin was more than just a statesman; he was an inventor and scientist who made lasting contributions to various fields. He invented the lightning rod, which protects buildings from lightning strikes. His invention of bifocal glasses helped people with vision problems, and the Franklin stove offered a more efficient way to heat homes. Franklin also conducted experiments that expanded our understanding of electricity. He introduced terms like “battery,” “conductor,” and “electrician,” which are still in use today. His work in electricity paved the way for the electrical revolution that followed and if you own a revolutionary idea of any kind pls check here for more details.
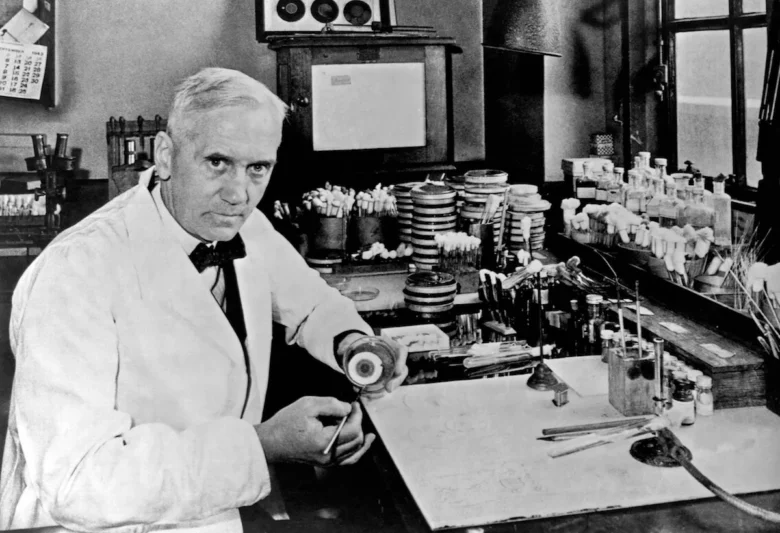
Alexander Fleming

Source: time.com
Fleming’s discovery of penicillin in 1928 marked a turning point in medical history. Before antibiotics, bacterial infections often meant a death sentence. Fleming’s accidental discovery of a mold that killed bacteria led to the development of antibiotics, saving countless lives. Penicillin treats a wide range of bacterial infections, from pneumonia to skin infections. His work earned him the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1945 and set the stage for the development of other antibiotics and antimicrobial drugs.
Conclusion
Each investor has made a lasting impact on society with their revolutionary ideas, products, and discoveries. Their tremendous achievements will be remembered for generations to come and will continue to inspire generations of future innovators. Without these pioneering individuals, our lives would look much different today – so let us take this time to recognize their accomplishments and thank them for all they have done.
