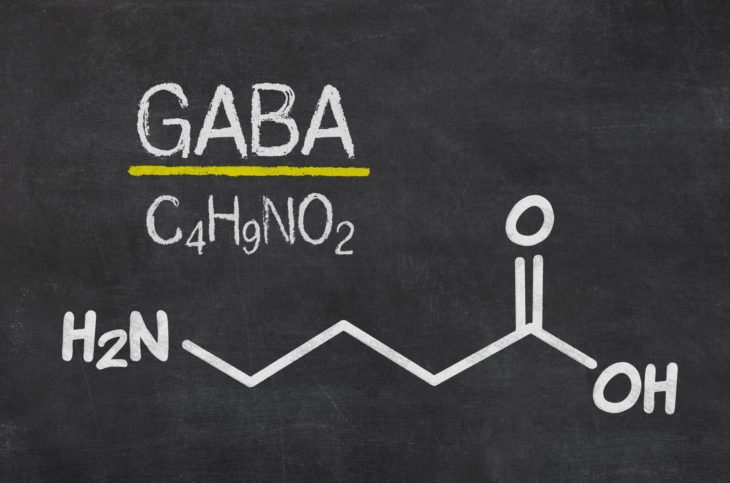
GABA supplement (Gamma-Aminobutyric acid) is a potent depressive neuroactive peptide that is found in the human brain tissue. It is sold as a dietary supplement and has become a very popular nootropic among its users. The GABA term refers to the chemical substance (NH2CH2CH2 CH2COOH).
GABA was discovered in 1950 by Roberts and Frankel, who found this nootropic as a part of the mammalian central nervous system. It acts like the stimulation of the inhibitory nerve, inhibitory synapse on crayfish muscle fibers in 1959. Also, GABA was first incorporated and was known as only the first plant-microbe metabolic product in 1883.
GABA plays a significant role in the healthy functioning of the body’s immune and endocrine systems as well as regulates the metabolism and appetite.
The body’s own GABA activity is vital for sleep. It enables your body and mind to relax and quickly fall asleep by improving a sleeping condition during the whole night. Having a low GABA amount may lead to Insomnia and Irregular Sleeping pattern that will lead to being restless, and make you out of focus or unproductive.
As like with the sleep, it can also affect you in being stressed or having anxiety. Moreover, GABA promotes excellent relaxation for the body and alleviates your mood. Most people also used GABA supplements as a natural aid to lower their blood pressure. There is some evidence saying that GABA may have an impact on reducing high blood pressure.
Source: Natural Stacks
Contents
Foods Rich in GABA
Alongside a GABA as a supplement, some foods may be a good source of such substance. These foods are rich with nutrients that may maintain your health, so by eating, you provide your body not only with a GABA but also with other useful supplements. According to the newest research, in this list, we may include whole grains or beans (brown rice, oatmeal, bread, etc.), fish, citrus fruits, spinach, mushrooms, potatoes, and even a white tea.
Uses and Benefits of GABA
Such popularity of GABA has grown because of its benefits that improve people’s cognitive and body functions. GABA works by blocking brain signals (neurotransmitters) and provides calmness.
It is believed that GABA helps to reduce anxiety and even depression symptoms as well as improve your daily mood. By bringing calmness, GABA improves your sleeping quality and helps to regulate your sleep cycle. Women users say that GABA reduces the symptoms of Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS). Attention deficit or hyperactivity disorder also may be treated by using a GABA supplement. It is one of the famous Nootropics of cognitive supplements.
Dosage
The correct dosage of GABA depends on several factors, such as the user’s age, health, and several other conditions. GABA is likely safe when taken correctly by mouth for a short period, up to 12 weeks. You may follow the label with the dosage instruction or start with the small quantity. Just make sure to supervise your body reactions not to take too much.
GABA supplement if available at Raw Powders. 100% Pure and No Additives, Gluten-Free, GMO-Free, and Suitable for Vegans and Vegetarians.

Source: NutraIngredients
GABA is the inhibitory neurotransmitter
Such as serotonin or dopamine, GABA is a neurotransmitter. Therefore, it ends chemical messages through the brain and nervous system. In other words, it participates in communication between neurons.
Its central role is to inhibit or reduce neuronal activity. Furthermore, it plays an essential role in the behavior, cognition, and response of the body to stress. Some researches show that GABA helps control fear and anxiety when neurons are overexcited.
Low levels of this neurotransmitter are associated with anxiety disorders, sleep problems, depression, and schizophrenia. Furthermore, It has been found that young neurons are more excitable than old ones, and this is due to the role that GABA exerts on the latter.
GABA contributes to motor control, vision, or regulates anxiety, among other cortical functions. Different drugs increase GABA levels in the brain and are used to treat epilepsy, Huntington’s disease, or to calm anxiety (for example, benzodiazepines).
However, one must bear in mind that little is known about the functions and processes in which GABA is involved. Therefore, it is rash to assume that its usefulness is what we have described earlier. Besides, this neurotransmitter intervenes to a greater or lesser extent in other communication dynamics between neurons in which other neurotransmitters have a more important role.
GABA’s relationship to fear and anxiety
The GABA was discovered in 1950 by Eugene Roberts and J. Awapara, and since then, various studies have been carried out to understand its relationship with anxiety disorders better.
In recent decades, research on GABA and benzodiazepines has been numerous, basically to seek treatments against the pathological alterations of fear and anxiety. These studies have concluded that GABA is involved in these emotions. Still, it does not appear that its role is other than that of an inhibitory modulator of other neurotransmitter systems.
Also, other studies have provided exciting conclusions as to how the effect of this neurotransmitter can reduce stress. In a published experiment, the Journal of Neuroscience showed that when individuals exercise regularly, the level of GABA neurons increases in the brain, which affects the ventral hippocampus, a region of the brain linked to the regulation of stress and anxiety. Another study, this time carried out jointly by the University of Boston and the University of Utah, found that there is also an increase in this neurotransmitter in yoga practitioners.

Source: WanderGlobe
How is GABA synthesized?
It is synthesized from the decarboxylation of glutamate. The process occurs in gabaergic neurons in the cerebellum, basal ganglia, and many areas of the cerebral cortex, also in the spinal cord. If the synthesis of this neurotransmitter is inhibited, convulsive attacks occur.
GABA receptors
GABA receptors are probably the most numerous in the mammalian nervous system. It is estimated that they are present in at least 30-40% of human nerve cells in the brain.
There are three types of receptors for GABA: GABA-A, GABA-B, and GABA-C. The latter is considered a subtype of the GABA-A receptor and is also called GABA-A rho.
The GABA-A receiver
The GABA-A is related to benzodiazepines such as Diazepam, barbiturates, or alcohol. It is the best-known receptor and is composed of five polypeptide subunits: α, β, γ, δ, ε, each with different functions.
The GABA-B receptor is metabotropic and is found in the plasma membrane of the pre and postsynaptic terminals. The GABA C receptor, like GABA-A, is ionotropic.

Source: nootropicgeek
Ionotropic and metabotropic receptors
Ionotropic receptors receive this name because they are coupled to an ionic channel, which when the ligand binds to them, the circuit opens, and an ion enters or exits through the channel. In the case of the GABA-A receptor, chlorine (Cl-) comes, which produces the inhibitory response. Its effect is fast because you have to open the channel to create the action.
Metabotropic receptors, such as GABA-B, are slower receptors and are coupled to G proteins. Such proteins, specifically in the case of this receptor, lead to the activation of potassium (K +) channels for depolarization of the cell.
